Short-term management of insomnia
Adult: 125-250 mcg at bedtime for up to 2 wk. Max: 500 mcg.
Elderly: Initially, 125 mcg at bedtime. Max: 250 mcg.
Elderly: Initially, 125 mcg at bedtime. Max: 250 mcg.
|
Indications and Dosage
Oral
Short-term management of insomnia Adult: 125-250 mcg at bedtime for up to 2 wk. Max: 500 mcg.
Elderly: Initially, 125 mcg at bedtime. Max: 250 mcg. |
|
Special Patient Group
Debilitated patients: Initially, 125 mcg at bedtime. Max: 250 mcg.
|
|
Hepatic Impairment
Severe: Initially, 125 mcg.
|
|
Administration
May be taken with or without food.
|
|
Contraindications
Pregnancy. Concomitant use w/ CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g. ketoconazole, itraconazole, nefazodone, several HIV protease inhibitors).
|
|
Special Precautions
Patient w/ signs and symptoms of depression, chronic pulmonary insufficiency and sleep apnoea. Patient w/ a history of alcoholism, drug abuse, or in patient w/ marked personality disorders. Long-term use may lead to dependence. Avoid abrupt withdrawal in long-term treatment. Renal and hepatic impairment. Elderly and debilitated patients. Lactation.
|
|
Adverse Reactions
Anterograde amnesia, abnormal thinking, behavioural changes, agitation, hallucinations, bizarre behaviour, depersonalisation; hypersensitivity reactions (e.g. angioedema); paradoxical reactions (e.g. hyperactive or aggressive behaviour); sleep-related activities (e.g. sleep-driving); drowsiness, headache, dizziness, ataxia, lightheadedness, nervousness, nausea, vomiting, confusion, cramps, depression, dermatitis, dreaming/nightmares, dysaesthesia, euphoria, fatigue, hepatic failure (fulminant), memory impairment, pain, paraesthesia, tachycardia, violent acts, visual disturbance, weakness, xerostomia, burning tongue/glossitis/stomatitis, chest pain, dysarthria, jaundice, libido changes, menstrual irregularities, pruritus, sedation, slurred speech, urinary incontinence, urinary retention.
Potentially Fatal: Anaphylaxis. |
|
Patient Counseling Information
May impair ability to drive or operate machinery.
|
|
Monitoring Parameters
Monitor daytime alertness, resp rate and behaviour profile.
|
|
Overdosage
Symptoms: Somnolence, confusion, impaired coordination, slurred speech, and ultimately, coma; resp depression, apnoea, seizures. Management: Perform immediate gastric lavage w/ maintenance of adequate airway. IV fluids may be administered. Flumazenil may be used as antidote.
|
|
Drug Interactions
Increased plasma concentrations w/ macrolide antibiotics, cimetidine, isoniazid, OCs and ranitidine.
Potentially Fatal: CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g. ketoconazole, itraconazole, nefazodone, several HIV protease inhibitors) may significantly increase plasma concentrations of triazolam. |
|
Food Interaction
Alcohol may enhance the CNS effects of triazolam. Increased plasma concentrations w/ grapefruit juice.
|
|
Action
Description: Triazolam binds to stereospecific benzodiazepine receptors on the postsynaptic GABA neuron at several sites w/in the CNS, including the limbic system, reticular formation. Enhancement of the inhibitory effect of GABA on neuronal excitability results by increased neuronal membrane permeability to Cl ions, which results in hyperpolarisation (a less excitable state) and stabilisation. Benzodiazepine receptors and effects appear to be linked to the GABA-A receptors.
Onset: 15-30 min. Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Rapidly and nearly completely absorbed from the GI tract. Time to peak plasma concentration: W/in 2 hr. Distribution: Volume of distribution: 0.6-1.7 L/kg. Plasma protein binding: Approx 89%. Metabolism: Hepatically via hydroxylation by CYP3A4 isoenzyme. Excretion: Via urine (approx 80%, mainly as conjugated metabolites and small amounts as unchanged drug). Plasma elimination half-life: 1.5-5.5 hr. |
|
Chemical Structure
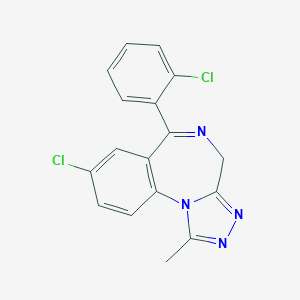 Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Database. Triazolam, CID=5556, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Triazolam (accessed on Jan. 23, 2020) |
|
Storage
Store between 20-25°C.
|
|
MIMS Class
|
|
ATC Classification
N05CD05 - triazolam ; Belongs to the class of benzodiazepine derivatives. Used as hypnotics and sedatives.
|
|
References
Anon. Triazolam. Lexicomp Online. Hudson, Ohio. Wolters Kluwer Clinical Drug Information, Inc. https://online.lexi.com. Accessed 27/11/2014. Buckingham R (ed). Triazolam. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference [online]. London. Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 27/11/2014. Halcion Tablet (Pharmacia and Upjohn Company). DailyMed. Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/. Accessed 27/11/2014. McEvoy GK, Snow EK, Miller J et al (eds). Triazolam. AHFS Drug Information (AHFS DI) [online]. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP). https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 27/11/2014.
|