Chronic hepatitis C
Adult: In patient with chronic hepatitis C genotype 1 or 4 with compensated liver disease: 150 mg once daily, in combination with other antivirals. Treatment duration varies according to regimen used.
|
Indications and Dosage
Oral
Chronic hepatitis C Adult: In patient with chronic hepatitis C genotype 1 or 4 with compensated liver disease: 150 mg once daily, in combination with other antivirals. Treatment duration varies according to regimen used.
|
|
Hepatic Impairment
Moderate or severe (Child-Pugh class B or C): Not recommended.
|
|
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity. Concomitant use with CYP3A4 inducers or inhibitors.
|
|
Special Precautions
Patient with hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, decompensated cirrhosis. Moderate to severe hepatic impairment. Not intended for use as monotherapy. Pregnancy and lactation.
|
|
Adverse Reactions
Significant: Photosensitivity, rash, pruritus.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: Hyperbilirubinaemia. Gastrointestinal disorders: Nausea, diarrhoea, constipation. General disorders and administration site conditions: Fatigue. Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: Myalgia. Nervous system disorders: Headache, dizziness. Psychiatric disorders: Insomnia. Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Dyspnoea. Potentially Fatal: Hepatitis B virus reactivation, resulting in fulminant hepatitis or hepatic failure (in patients with HBV co-infection); hepatic decompensation and hepatic failure, symptomatic bradycardia. |
|
Patient Counseling Information
May impair ability to drive or operate machinery.
|
|
Monitoring Parameters
Monitor CBC, INR, LFT, serum creatinine, HCV-RNA at baseline and during therapy. Obtain hepatitis B surface antigen (HbsAg) and hepatitis B core antibody (anti-HBc) prior to initiation of therapy to test for evidence of current or prior HBV infection. Perform pregnancy test and ensure proper use of birth control prior to therapy.
|
|
Drug Interactions
Increased plasma concentration with antiarrhythmic agents (e.g. disopyramide, flecainide, mexiletine). Increased anticoagulant effect of warfarin.
Potentially Fatal: Decreased plasma concentration and therapeutic effect with moderate or strong CYP3A4 inducers (e.g. carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, rifampicin). Increased plasma levels with moderate or potent CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g. ketoconazole). May increase the concentrations of P-glycoprotein substrates (e.g. doxorubicin), organic anion transport polypeptides, ciclosporin. May cause symptomatic bradycardia when given with amiodarone. |
|
Food Interaction
Increased absorption with food. Decreased serum concentration with St John’s wort. Increased serum concentration with milk thistle.
|
|
Action
Description: Simeprevir is a hepatitis C virus (HCV) nonstructural protein 3/4A (NS3/4A) serine protease inhibitor. It binds to the NS3/4A protease active site, thereby inhibiting viral replication activity.
Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Increased absorption with food. Bioavailability: 62%. Time to peak plasma concentration: 4-6 hr. Distribution: Plasma protein binding: >99.9%, to albumin and α1-acid glycoprotein. Metabolism: Undergoes oxidative metabolism in the liver mainly by CYP3A4 enzyme, to unchanged drug and metabolites. Excretion: Mainly via faeces (approx 91%); urine (<1%). Terminal elimination half-life: 41 hours. |
|
Chemical Structure
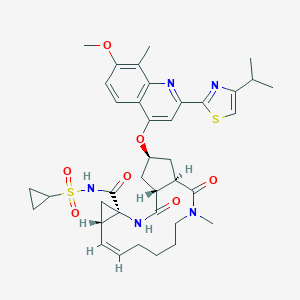 Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Database. Simeprevir, CID=24873435, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Simeprevir (accessed on Jan. 23, 2020) |
|
Storage
Store below 30°C. Protect from light.
Any unused portions should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements. |
|
MIMS Class
|
|
ATC Classification
J05AP05 - simeprevir ; Belongs to the class of antivirals for treatment of HCV infections. Used in the treatment of hepatitis C viral infections.
|
|
References
Anon. Simeprevir. Lexicomp Online. Hudson, Ohio. Wolters Kluwer Clinical Drug Information, Inc. https://online.lexi.com. Accessed 01/02/2018. Buckingham R (ed). Simeprevir. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference [online]. London. Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 01/02/2018. Joint Formulary Committee. Simeprevir. British National Formulary [online]. London. BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 01/02/2018. McEvoy GK, Snow EK, Miller J et al (eds). Simeprevir Sodium. AHFS Drug Information (AHFS DI) [online]. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP). https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 01/02/2018. Olysio Capsule (Janssen Products LP). DailyMed. Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/. Accessed 01/02/2018.
|