Type 2 diabetes mellitus
Adult: As monotherapy or in combination with other antidiabetic agents: 50 mg bid. Max: 100 mg daily. Refer to specific product guidelines for further information on use with other antidiabetic agents.
|
Indications and Dosage
Oral
Type 2 diabetes mellitus Adult: As monotherapy or in combination with other antidiabetic agents: 50 mg bid. Max: 100 mg daily. Refer to specific product guidelines for further information on use with other antidiabetic agents.
|
|
Renal Impairment
Moderate to severe and ESRD patients requiring haemodialysis: 50 mg once daily.
|
|
Hepatic Impairment
Not recommended.
|
|
Administration
May be taken with or without food.
|
|
Special Precautions
Patient with a history of pancreatitis. Not recommended for use in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus or diabetic ketoacidosis; New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class IV. Moderate to severe renal impairment, including ESRD patients requiring haemodialysis. Not recommended for use in patients with hepatic impairment, including those with pre-treatment ALT or AST >3 times the ULN. Not considered as a substitute for insulin in patients that require them.
|
|
Adverse Reactions
Significant: Severe and disabling arthralgia, bullous and exfoliative skin lesions (including bullous pemphigoid), acute pancreatitis; hypoglycaemia (particularly during combination therapy with sulfonylureas). Rarely, hepatic dysfunction (e.g. hepatitis, jaundice, increase in AST or ALT 3 times the upper limit of normal [ULN]).
Gastrointestinal disorders: Nausea, constipation. General disorders and administration site conditions: Fatigue, peripheral oedema. Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: Myalgia. Nervous system disorders: Dizziness, headache. Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Rarely, upper respiratory tract infection, nasopharyngitis. Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Urticaria. |
|
Patient Counseling Information
This drug may cause dizziness, if affected, do not drive or operate machinery.
|
|
Monitoring Parameters
Monitor LFTs (before initiation, every 3 months for the 1st year of treatment, and as necessary thereafter), renal function (before initiation and as necessary thereafter), HbA1c (twice a year for those who have stable glycaemic control and are meeting the treatment goals, quarterly for those not meeting the treatment goals or with changes in therapy), plasma glucose. Assess for signs and symptoms of pancreatitis (e.g. persistent severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, anorexia), and heart failure.
|
|
Overdosage
Symptoms: Muscle pain, mild and transient paraesthesia, fever, oedema (e.g. feet oedema), transient increase in lipase levels; increased creatine phosphokinase (CPK), AST, C-reactive protein (CRP), and myoglobin levels. Management: Supportive treatment.
|
|
Drug Interactions
Increased risk of hypoglycaemia during combination therapy with sulfonylureas; consider lowering the dose of sulfonylureas. May increase the risk of angioedema with ACE-inhibitors. Thiazides, corticosteroids, thyroid products, and sympathomimetics may decrease the hypoglycaemic effect of vildagliptin.
|
|
Action
Description:
Mechanism of Action: Vildagliptin is an inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4), it causes an increase in fasting and postprandial endogenous levels of the incretin hormones GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide 1) and GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide). Duration: DPP-4 inhibition (>50%): Approx 14 hours. Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Rapidly absorbed. Bioavailability: 85%. Time to peak plasma concentration: Approx 1.75 hours (fasted); 2.5 hours (fed). Distribution: Equally distributed between plasma and RBC. Plasma protein binding: 9.3%. Metabolism: Undergoes hydrolysis in the kidney to LAY151 (major inactive metabolite of the cyano moiety) and other metabolites. Excretion: Via urine (approx 85%; 23% as unchanged drug); faeces (15%). Elimination half-life: Approx 3 hours. |
|
Chemical Structure
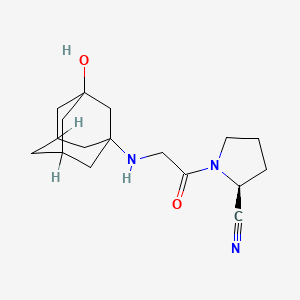 Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 6918537, Vildagliptin. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Vildagliptin. Accessed Oct. 25, 2023. |
|
Storage
Store below 30°C. Protect from moisture.
|
|
MIMS Class
|
|
ATC Classification
A10BH02 - vildagliptin ; Belongs to the class of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors. Used in the treatment of diabetes.
|
|
References
Anon. Vildagliptin. Lexicomp Online. Hudson, Ohio. Wolters Kluwer Clinical Drug Information, Inc. https://online.lexi.com. Accessed 04/03/2022. Buckingham R (ed). Vildagliptin. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference [online]. London. Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 04/03/2022. Galvus (Novartis Corporation [Malaysia] Sdn. Bhd.). National Pharmaceutical Regulatory Agency - Ministry of Health Malaysia. https://www.npra.gov.my. Accessed 04/03/2022. Galvus 50 mg Tablets (Novartis Pharmaceuticals UK Limited). MHRA. https://products.mhra.gov.uk. Accessed 04/03/2022. Joint Formulary Committee. Vildagliptin. British National Formulary [online]. London. BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 04/03/2022. Novartis New Zealand Limited. Galvus 50 mg Tablets data sheet 01 July 2020. Medsafe. http://www.medsafe.govt.nz. Accessed 04/03/2022.
|