Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Adult: Initially, 267 mg tid for 7 days, then increase dose to 534 mg tid for 7 days, then to usual maintenance dose: 801 mg tid. Max: 2403 mg daily. Adjust dosage according to toxicity.
|
Indications and Dosage
Oral
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis Adult: Initially, 267 mg tid for 7 days, then increase dose to 534 mg tid for 7 days, then to usual maintenance dose: 801 mg tid. Max: 2403 mg daily. Adjust dosage according to toxicity.
|
||||
|
Special Patient Group
Patient concomitantly using strong CYP1A2 inhibitors (e.g. enoxacin, fluvoxamine): 267 mg tid.
Patient concomitantly using ciprofloxacin at a dosage of 750 mg bid: 534 mg tid. |
||||
|
Renal Impairment
ESRD requiring haemodialysis: Contraindicated.
|
||||
|
Hepatic Impairment
Severe (Child-Pugh class C): Contraindicated.
|
||||
|
Contraindications
Severe hepatic and renal impairment, ESRD requiring haemodialysis.
|
||||
|
Special Precautions
Smokers. Mild to moderate hepatic and renal impairment. Pregnancy and lactation. Patient taking fluvoxamine and ciprofloxacin.
|
||||
|
Adverse Reactions
Significant: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, dyspepsia, GERD, abdominal pain, photosensitivity, weight loss, dizziness, increased ALT/AST, angioedema. Rarely, hyperbilirubinaemia.
Gastrointestinal disorders: Constipation, flatulence, gastritis. General disorders and administration site conditions: Fatigue, asthenia, lethargy, non-cardiac chest pain. Investigations: Increased γ-glutamyl transferase. Metabolism and nutrition disorders: Anorexia, decreased appetite. Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: Myalgia, arthralgia. Nervous system disorders: Headache, dysgeusia. Psychiatric disorders: Insomnia, somnolence. Renal and urinary disorders: UTI. Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Dyspnoea, cough, upper respiratory tract infection. Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Rash, pruritus, erythema, dry skin, sunburn. Vascular disorders: Hot flush. |
||||
|
Patient Counseling Information
Avoid smoking. This drug may cause dizziness and fatigue, if affected, do not drive or operate machinery. Avoid excessive exposure to sun and UV light.
|
||||
|
Monitoring Parameters
Perform LFT before initiation of treatment, monthly for the 1st 6 months and quarterly, thereafter. Monitor weight; signs and symptoms of gastrointestinal and photosensitivity reactions.
|
||||
|
Drug Interactions
Increased toxicity with strong (e.g. fluvoxamine) and moderate (e.g. ciprofloxacin) CYP1A2 inhibitors. Decreased efficacy with CYP1A2 inducers (e.g. omeprazole).
|
||||
|
Food Interaction
Decreased absorption with food. May increase toxicity with grapefruit juice.
|
||||
|
Action
Description:
Mechanism of Action: Pirfenidone, a synthetic pyridone, is an antifibrotic agent. Its exact mechanism of action is still unknown. In idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, it may decrease the amount of pro-inflammatory cells [e.g. interleukin-1-β (IL-1β), IL-6, tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)] and the production of fibroblast and of fibrosis-associated proteins and cytokines. It may also decrease accumulation of extracellular matrix and lung fibrosis due to transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) and platelet derived growth factor (PDGF). Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Decreased absorption with food. Time to peak plasma concentration: 30 minutes to 4 hours. Distribution: Volume of distribution: Approx 59-71 L. Plasma protein binding: 50-58% mainly to albumin. Metabolism: Metabolised in the liver mainly by CYP1A2 and to a lesser extent by CYP2C9, 2C19, 2D6 and 2E1 into metabolites including 5-carboxy-pirfenidone. Excretion: Mainly via urine (approx 80%; >95% as 5-carboxy-pirfenidone and <1% as unchanged drug). Terminal elimination half-life: Approx 3 hours. |
||||
|
Chemical Structure
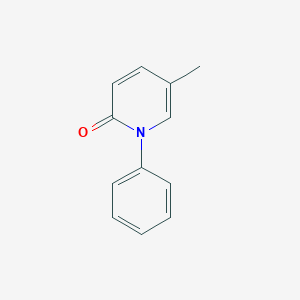 Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Database. Pirfenidone, CID=40632, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Pirfenidone (accessed on Jan. 22, 2020) |
||||
|
Storage
Store at 25°C.
|
||||
|
MIMS Class
|
||||
|
ATC Classification
L04AX05 - pirfenidone ; Belongs to the class of other immunosuppressants.
|
||||
|
References
Anon. Pirfenidone. Lexicomp Online. Hudson, Ohio. Wolters Kluwer Clinical Drug Information, Inc. https://online.lexi.com. Accessed 30/01/2018. Buckingham R (ed). Pirfenidone. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference [online]. London. Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 30/01/2018. Esbriet 267 mg Hard Capsules (Roche Products Limited). eMC. https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/. Accessed 30/01/2018. Esbriet 801 mg Film-coated Tablets (Roche Products Limited). eMC. https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/. Accessed 30/01/2018. Esbriet Capsule; Esbriet Tablet, Coated (Genentech, Inc.). DailyMed. Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/. Accessed 30/01/2018. Joint Formulary Committee. Pirfenidone. British National Formulary [online]. London. BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 30/01/2018. McEvoy GK, Snow EK, Miller J et al (eds). Pirfenidone. AHFS Drug Information (AHFS DI) [online]. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP). https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 30/01/2018. Rossi S (ed). Pirfenidone. Australian Medicines Handbook [online]. Adelaide. Australian Medicines Handbook Pty Ltd. https://amhonline.amh.net.au. Accessed 30/01/2018.
|