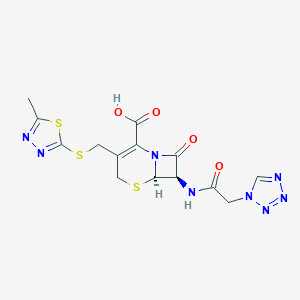
Susceptible infections
Adult: Mild: 0.25-0.5 g 8 hrly. Moderate to severe: 0.5-1 g 6-8 hrly. Severe, life-threatening: 1-1.5 g 6 hrly. Max: 12 g daily. All doses to be given by deep IM inj, slow IV inj over 3-5 min, or intermittent or continuous IV infusion.
Child: >1 yr 25-50 mg/kg daily in 3 or 4 divided doses to be given by deep IM inj, slow IV inj over 3-5 min, or intermittent or continuous IV infusion. Max: 100 mg/kg daily in divided doses for severe infections.
Child: >1 yr 25-50 mg/kg daily in 3 or 4 divided doses to be given by deep IM inj, slow IV inj over 3-5 min, or intermittent or continuous IV infusion. Max: 100 mg/kg daily in divided doses for severe infections.
Parenteral
Acute uncomplicated urinary tract infections
Adult: 1 g 12 hrly to be given by deep IM inj, slow IV inj over 3-5 min, or intermittent or continuous IV infusion. Max: 12 g daily.
Child: >1 yr 25-50 mg/kg daily in 3 or 4 divided doses to be given by deep IM inj, slow IV inj over 3-5 min, or intermittent or continuous IV infusion. Max: 100 mg/kg daily in divided doses for severe infections.
Child: >1 yr 25-50 mg/kg daily in 3 or 4 divided doses to be given by deep IM inj, slow IV inj over 3-5 min, or intermittent or continuous IV infusion. Max: 100 mg/kg daily in divided doses for severe infections.
Parenteral
Pneumonia
Adult: 500 mg 12 hrly to be given by deep IM inj, slow IV inj over 3-5 min, or intermittent or continuous IV infusion. Max: 12 g daily.
Child: >1 yr 25-50 mg/kg daily in 3 or 4 divided doses to be given by deep IM inj, slow IV inj over 3-5 min, or intermittent or continuous IV infusion. Max: 100 mg/kg daily in divided doses for severe infections.
Child: >1 yr 25-50 mg/kg daily in 3 or 4 divided doses to be given by deep IM inj, slow IV inj over 3-5 min, or intermittent or continuous IV infusion. Max: 100 mg/kg daily in divided doses for severe infections.
Parenteral
Prophylaxis of surgical infections
Adult: 1 g given 30-60 min prior to surgery, followed by 0.5-1 g during surgery for lengthy procedures, then 0.5-1 g 6-8 hrly after surgery for 24 hr or up to 5 days. All doses to be given by deep IM inj, slow IV inj over 3-5 min, or intermittent or continuous IV infusion.




 Sign Out
Sign Out