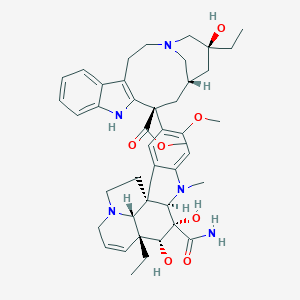
Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
Adult: Resistant to other drugs: Initially, 3 mg/m2. Dose may be increased in increments of 0.5 mg/m2 at weekly intervals if granulocyte count is >1,500 cells/mm3, platelet count is >100,000 cells/mm3, and if there is no abdominal pain. Usual dose: 3-4 mg/m2 weekly. Max: 4 mg/m2 weekly. Doses to be given via freely running infusion or directly into a vein over 1-3 minutes.
Child: Resistant to other drugs: Initially, 4 mg/m2. Dose may be increased in increments of 0.5 mg/m2 at weekly intervals if granulocyte count is >1,500 cells/mm3, platelet count is >100,000 cells/mm3, and if there is no abdominal pain. Usual dose: 4-5 mg/m2 weekly.
Child: Resistant to other drugs: Initially, 4 mg/m2. Dose may be increased in increments of 0.5 mg/m2 at weekly intervals if granulocyte count is >1,500 cells/mm3, platelet count is >100,000 cells/mm3, and if there is no abdominal pain. Usual dose: 4-5 mg/m2 weekly.
Intravenous
Blastic phase chronic myeloid leukaemia
Adult: Initially, 3 mg/m2. Dose may be increased in increments of 0.5 mg/m2 at weekly intervals if granulocyte count is >1,500 cells/mm3, platelet count is >100,000 cells/mm3, and if there is no abdominal pain. Usual dose: 3-4 mg/m2 weekly. Max: 4 mg/m2 weekly. Doses to be given via freely running infusion or directly into a vein over 1-3 minutes.
Intravenous
Breast carcinoma
Adult: Advanced and unresponsive to appropriate endocrine surgery and/or hormonal therapy: Initially, 3 mg/m2. Dose may be increased in increments of 0.5 mg/m2 at weekly intervals if granulocyte count is >1,500 cells/mm3, platelet count is >100,000 cells/mm3, and if there is no abdominal pain. Usual dose: 3-4 mg/m2 weekly. Max: 4 mg/m2 weekly. Doses to be given via freely running infusion or directly into a vein over 1-3 minutes.
Intravenous
Malignant melanoma
Adult: Unresponsive to other forms of therapy: Initially, 3 mg/m2. Dose may be increased in increments of 0.5 mg/m2 at weekly intervals if granulocyte count is >1,500 cells/mm3, platelet count is >100,000 cells/mm3, and if there is no abdominal pain. Usual dose: 3-4 mg/m2 weekly. Max: 4 mg/m2 weekly. Doses to be given via freely running infusion or directly into a vein over 1-3 minutes.




 Sign Out
Sign Out