Oedema
Adult: 150-250 mg bid, after breakfast and lunch. Maintenance: Doses may be given on alternate days. Max: 300 mg daily.
Oral
Hypertension
Adult: In combination w/ other diuretics (e.g. hydrochlorothiazide): Initially, 50 mg daily.
|
Indications and Dosage
Oral
Oedema Adult: 150-250 mg bid, after breakfast and lunch. Maintenance: Doses may be given on alternate days. Max: 300 mg daily. Oral Hypertension Adult: In combination w/ other diuretics (e.g. hydrochlorothiazide): Initially, 50 mg daily.
|
|
Renal Impairment
Severe: Contraindicated.
|
|
Hepatic Impairment
Severe: Contraindicated.
|
|
Administration
Should be taken with food.
|
|
Contraindications
Pre-existing or drug-induced hyperkalaemia, anuria, Addison's disease. Severe renal and hepatic impairment. Concomitant use w/ other K-sparing agents, K supplements.
|
|
Special Precautions
Patient w/ DM, hyperuricaemia or gout, history of renal calculi. Renal and hepatic impairment. Pregnancy and lactation.
|
|
Adverse Reactions
Photosensitivity reactions, blood dyscrasias, renal calculi, megaloblastic anaemia, reversible renal failure, increase in uric acid concentration, GI disturbances (e.g. nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea), hypotension, dizziness, weakness, headache, dry mouth, muscle cramps, anaphylaxis, rash.
Potentially Fatal: Hyperkalaemia. |
|
Patient Counseling Information
May cause a blue fluorescence of the urine under certain light conditions.
|
|
Monitoring Parameters
Monitor serum electrolytes (esp K) frequently, BP, renal function.
|
|
Overdosage
Symptoms: Electrolyte imbalance esp hyperkalaemia, GI disturbances (e.g. nausea, vomiting), weakness, hypotension. Management: Induced gastric lavage or emesis. Admin pressor agents (e.g. norepinephrine) for severe hypotension. May perform dialysis.
|
|
Drug Interactions
May reduce antihypertensive effect w/ NSAIDs. May increase hyperkalaemic effect of ACE inhibitors. May increase risk of lithium toxicity. Increased risk of postural hypotension w/ TCAs. Increased risk of hyponatraemia w/ carbamazepine. May increase nephrotoxic effect w/ indometacin.
Potentially Fatal: May increase risk of hyperkalaemia w/ other K-sparing agents, K supplements. |
|
Lab Interference
May interfere w/ the methods of enzyme assay that depend on fluorometry (e.g. determination of lactic dehydrogenase activity). Interferes w/ fluorometric assay of quinidine and bioassay of folic acid.
|
|
Action
Description: Triamterene is a weak K-sparing diuretic which appears to act mainly on the distal renal tubules. It increases the excretion of Na, Mg, Ca, bicarbonate and decreases K excretion. It adds to the natriuretic but reduces the kaliuretic effects of other diuretics.
Onset: Diuresis: 2-4 hr. Duration: Diuresis: 7-9 hr. Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Variably but fairly rapidly absorbed from the GI tract. Bioavailability: Approx 50%. Time to peak plasma concentration: 3 hr. Distribution: Crosses the placenta; enters breast milk. Plasma protein binding: Approx 60%. Metabolism: Extensively metabolised by CYP1A2 isoenzyme to the sulfate conjugate of hydroxytriamterene. Excretion: Via urine (21% to <50%, mainly as metabolites). Plasma half-life: Approx 2 hr. |
|
Chemical Structure
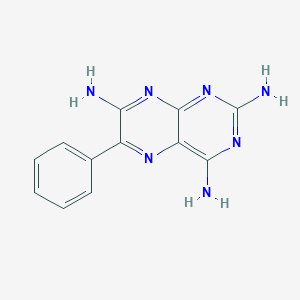 Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Database. Triamterene, CID=5546, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Triamterene (accessed on Jan. 23, 2020) |
|
Storage
Store between 15-30°C.
|
|
MIMS Class
|
|
ATC Classification
C03DB02 - triamterene ; Belongs to the class of other potassium-sparing agents. Used as diuretics.
|
|
References
Anon. Triamterene. Lexicomp Online. Hudson, Ohio. Wolters Kluwer Clinical Drug Information, Inc. https://online.lexi.com. Accessed 12/11/2014. Buckingham R (ed). Triamterene. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference [online]. London. Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 12/11/2014. Dyrenium Capsule (WellSpring Pharmaceutical Corporation). DailyMed. Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/. Accessed 12/11/2014. Joint Formulary Committee. Triamterene. British National Formulary [online]. London. BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 12/11/2014. McEvoy GK, Snow EK, Miller J et al (eds). Triamterene. AHFS Drug Information (AHFS DI) [online]. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP). https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 12/11/2014.
|