Psychomotor agitation
Adult: As short-term adjunctive management: 100-200 mg 4 times daily.
Oral
Agitation, Restlessness
Elderly: Initially, 25 mg 4 times daily, may increase to 50 mg 4 times daily, if necessary.
|
Indications and Dosage
Oral
Psychomotor agitation Adult: As short-term adjunctive management: 100-200 mg 4 times daily. Oral Agitation, Restlessness Elderly: Initially, 25 mg 4 times daily, may increase to 50 mg 4 times daily, if necessary.
|
|
Contraindications
Comatose states, CNS depression, phaeochromocytoma. Pregnancy and lactation.
|
|
Special Precautions
Patient with history of jaundice, blood dyscrasias, severe respiratory disease, Parkinsonism, epilepsy or conditions predisposing to seizures, diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, depression, myasthenia gravis, prostatic hypertrophy, personal or family history of angle-closure glaucoma, CV disease, family history of QT prolongation, risk factors for stroke, and venous thromboembolism. Renal and hepatic impairment. Elderly (including those with dementia-related psychosis). Avoid abrupt withdrawal.
|
|
Adverse Reactions
Significant: Venous thromboembolism (e.g. pulmonary embolism, DVT), extrapyramidal symptoms (e.g. dystonia, tremor, tardive dyskinesia, akathisia), impaired body core temperature, QT prolongation, photosensitisation, withdrawal symptoms.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: Haemolytic anaemia. Eye disorders: Corneal and lens opacities; purplish pigmentation of skin, cornea, conjunctiva, retina. Gastrointestinal disorders: Gastrointestinal disturbances. General disorders and administration site conditions: Hypothermia. Hepatobiliary disorders: Jaundice (including cholestatic jaundice). Investigations: Weight gain, increased prolactin levels. Nervous system disorders: Drowsiness, convulsions, headache, dizziness, anticholinergic symptoms (e.g. dry mouth, constipation, micturition difficulties, blurred vision). Psychiatric disorders: Apathy, excitement, confusional states. Reproductive system and breast disorders: Menstrual disturbances, galactorrhoea, gynaecomastia, impotence. Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Nasal congestion. Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Rash, contact sensitisation. Vascular disorders: Hypotension. Potentially Fatal: Rarely, neuroleptic malignant syndrome. |
|
Patient Counseling Information
This drug may cause drowsiness, if affected, do not drive or operate machinery. Avoid direct sunlight.
|
|
Monitoring Parameters
Perform CBC if unexplained fever or infection develops. Monitor ECG if clinically indicated; prolactin levels (at baseline, at 6 months then annually).
|
|
Overdosage
Symptoms: Drowsiness, confusion, hypotension, hypothermia, convulsions, coma, extrapyramidal symptoms. Rarely, respiratory depression, rhabdomyolysis, renal failure, cardiac effects (e.g. sinus tachycardia, QT and QRS prolongation, ventricular tachycardia, fibrillation, AV block, bundle branch block, torsades de pointes). Management: Administer activated charcoal (50 g for adults) or perform gastric lavage (in adults) within 1 hour of ingestion. Maintain adequate ventilation and a clear airway. Monitor asymptomatic patients for at least 4 hours after ingestion. Monitor blood pressure, pulse; ECG and cardiac rhythm (in symptomatic patients). Correct hypothermia, acid base and metabolic disturbances, hypotension. In case of persistent severe hypotension, may administer dopamine (2-10 mcg/kg/min) or dobutamine (2.5-10 mcg/kg/min). May consider the use of IV diazepam (0.1-0.3 mg/kg) or lorazepam (4 mg in adults). For unresponsive fits or seizures, may consider using phenytoin (loading dose: 15 mg/kg via IV infusion), if seizures persist, may consider intubation, paralysis and ventilation. In case of acute dystonic reactions, may administer procyclidine (5-10 mg in adults) or benztropine (1-2 mg), or diazepam (0.1-0.3 mg/kg).
|
|
Drug Interactions
May potentiate anticholinergic adverse effects with anti-parkinsonian drugs. May antagonise effects of sulfonylureas. May lower the convulsive threshold of antiepileptics. Enhanced hypotensive effect with antihypertensives (e.g. calcium channel blockers). Enhanced sedative effect with anxiolytics and hypnotic drugs. Increased plasma concentration with ritonavir. Increased risk of extrapyramidal effects with metoclopramide, lithium, phenothiazines. tetrabenazine. Increased CNS toxicity with sibutramine. Enhanced effect with cimetidine. Reduced antipsychotic effect with memantine. Enhanced sedative effect with opioid analgesics. Increased risk of convulsions with tramadol. Increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias including torsades de pointes with drugs known to prolong QT interval (e.g. quinidine, disopyramide, amiodarone, sotalol, erythromycin, amitriptyline, maprotiline, haloperidol, pimozide, terfenadine, cisapride, bretylium, quinine. Reduced absorption with antacids.
|
|
Food Interaction
Enhanced sedative effect with alcohol.
|
|
Action
Description: Promazine is a phenothiazine that has selective depressant effect on the CNS centres responsible for the control of wakefulness and behaviour. It also has α-adrenergic blocking, anticholinergic and dopamine inhibitory activities.
Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Distribution: Widely distributed in the body and crosses the blood-brain barrier. Crosses the placenta, enters breast milk. Metabolism: Extensively metabolised in the liver; undergoes first-pass metabolism in the gut wall. Excretion: Via urine and faeces (as metabolites). |
|
Chemical Structure
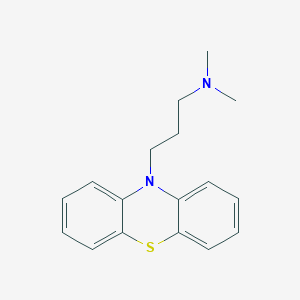 Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 4926, Promazine. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Promazine. Accessed Sept. 25, 2020. |
|
Storage
Store below 25°C. Protect from light.
|
|
MIMS Class
|
|
ATC Classification
N05AA03 - promazine ; Belongs to the class of phenothiazine antipsychotics with aliphatic side-chain.
|
|
References
Buckingham R (ed). Promazine. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference [online]. London. Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 04/08/2020. Joint Formulary Committee. Promazine Hydrochloride. British National Formulary [online]. London. BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 04/08/2020. Promazine 50 mg Film-Coated Tablets (Teva UK Limited). MHRA. https://products.mhra.gov.uk/. Accessed 04/08/2020. Promazine Hydrochloride 25 mg/5 mL Oral Syrup (Rosemont Pharmaceuticals Limited). MHRA. https://products.mhra.gov.uk/. Accessed 04/08/2020.
|