Atypical depression
Adult: Initially, 15 mg tid, increase to 4 times daily after 2 weeks according to response. Gradually reduce to usual maintenance dose: 15 mg every other day.
|
Indications and Dosage
Oral
Atypical depression Adult: Initially, 15 mg tid, increase to 4 times daily after 2 weeks according to response. Gradually reduce to usual maintenance dose: 15 mg every other day.
|
|
Special Patient Group
Hospitalised patients: Up to 30 mg tid.
|
|
Renal Impairment
Severe: Contraindicated.
|
|
Hepatic Impairment
Contraindicated.
|
|
Contraindications
Cerebrovascular disease, phaeochromocytoma, abnormal LFTs or history of hepatic disease. Hepatic and severe renal impairment. Within 10 days of use with general anaesthesia for elective surgery. Concomitant or within 14 days of discontinuing treatment with MAOIs, bupropion, and SSRIs. Concomitant use with dextromethorphan, CNS depressants (e.g. alcohol, pethidine), guanethidine. Tyramine-rich food.
|
|
Special Precautions
Patient with major depressive disorder, and other psychiatric disorders, bipolar disorder, risk for hypotension, hypertension, cerebrovascular disease, CV disease, diabetes mellitus, angle-closure glaucoma, hypovolaemia, risk or history of seizure, hyperthyroidism. Elderly. Children, adolescent and young adults. Pregnancy and lactation. Avoid abrupt withdrawal and dose reduction.
|
|
Adverse Reactions
Significant: Suicidality, CNS depression, postural hypotension, shift to hypomania or mania, intracranial bleeding, sensitisation to insulin, pyridoxine deficiency, withdrawal syndrome.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: Blood dyscrasias. Cardiac disorders: Arrhythmias. Eye disorders: Blurred vision, nystagmus, glaucoma. Gastrointestinal disorders: Nausea, vomiting, dry mouth, constipation. General disorders and administration site conditions: Weakness, fatigue, oedema, sweating. Investigations: Elevated serum transaminases, increased weight. Metabolism and nutrition disorders: Hypermetabolic syndrome, hypo/hypernatraemia, increased appetite. Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: Twitching, muscle tremor, lupus-like illness. Nervous system disorders: Dizziness, drowsiness, myoclonic movement, hyperreflexia, headache, paraesthesia, peripheral neuritis, convulsions, palilalia. Psychiatric disorders: Insomnia, nervousness, euphoria, behavioural changes, jitteriness, confusion, hallucinations. Renal and urinary disorders: Difficulty in micturition. Reproductive system and breast disorders: Impotence, delayed ejaculation. Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Rash, pruritus, purpura. Potentially Fatal: Hypertensive crises associated with intracranial bleeding. Rarely, progressive necrotising hepatocellular damage, neuroleptic malignant syndrome. |
|
Patient Counseling Information
This drug may impair cognitive ability, if affected, do not drive or operate machinery.
|
|
Monitoring Parameters
Monitor blood pressure, blood glucose, heart rate, renal function and LFT. Monitor for mental status, worsening of depression, suicidality, and unusual changes in behaviour prior to initiation of therapy and every dose titration.
|
|
Overdosage
Symptoms: Hypomania, euphoria, coma with hypotension or acute hypertension with or without subarachnoid haemorrhage, extra-pyramidal symptoms; agitation, convulsions, cool and clammy skin, diaphoresis, dizziness, drowsiness, faintness, hallucinations, severe headache, hyperactivity, hyperpyrexia, rapid and irregular pulse, irritability, opisthotonos, precordial pain, respiratory depression and failure, rigidity, trismus. Management: Symptomatic and supportive treatment. Perform gastric lavage with charcoal slurry. Support respiration by airway management, supplemental oxygen and mechanical ventilation if necessary. Consider IV therapy to maintain fluid and electrolyte balance, hypotension, and vascular collapse. May administer phentolamine IV for hypertension; slow IV diazepam inj for CNS stimulation.
|
|
Drug Interactions
May potentiate the effects of antihypertensives (e.g. β-blockers, thiazide diuretics), antimuscarinics, hypoglycaemic agents, anti-Parkinson agents, and local anaesthetics.
Potentially Fatal: Hypertensive crises with other MAOIs, sympathomimetics (e.g. amphetamines, cocaine, dopamine, ephedrine, epinephrine, norepinephrine, methylphenidate) and related compound (e.g. levodopa, methyldopa). Serotonin syndrome with SSRIs, SNRIs, and dextromethorphan. May potentiate the effects of CNS depressants and certain narcotics (e.g. pethidine). Increased hypotensive effect with spinal anaesthesia. Increased blood pressure with bupropion, buspirone, guanethidine. Hypertensive crises and fatal reactions with dibenzazepine derivatives (e.g. TCAs, carbamazepine, perphenazine). |
|
Food Interaction
Hypertensive crises with high concentration of tyramine, dopamine, phenylalanine, tyrosine, caffeine and chocolate. Behavioural and neurologic symptoms with high concentration of tryptophan. May potentiate the effects of alcohol.
|
|
Action
Description: Phenelzine inhibits both type A and type B monoamine oxidase (MAO), an enzyme responsible for the breakdown of biogenic amines. The exact mechanism of action has not been fully understood, but it is though that the increase in endogenous concentration of amine neurotransmitters (e.g. norepinephrine, dopamine and serotonin) within the CNS causes its antidepressant effect.
Onset: ≥4 weeks. Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Time to peak plasma concentration: 43 minutes. Metabolism: Extensively metabolised primarily via oxidation by MAO and via acetylation into N2-acetylphenelzine (minor pathway). Excretion: Mainly via urine (73%, as phenylacetic acid and parahydroxyphenylacetic acid metabolites). Elimination half-life: 11.6 hours. |
|
Chemical Structure
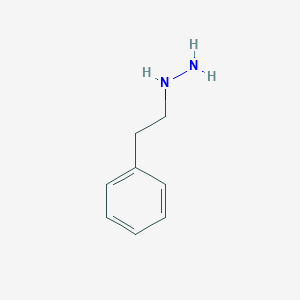 Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Database. Phenelzine, CID=3675, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Phenelzine (accessed on Jan. 22, 2020) |
|
Storage
Store between 2-8°C. Do not freeze.
|
|
MIMS Class
|
|
ATC Classification
N06AF03 - phenelzine ; Belongs to the class of non-selective monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Used in the management of depression.
|
|
References
Anon. Phenelzine. Lexicomp Online. Hudson, Ohio. Wolters Kluwer Clinical Drug Information, Inc. https://online.lexi.com. Accessed 17/10/2017. Buckingham R (ed). Phenelzine Sulfate. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference [online]. London. Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 17/10/2017. Joint Formulary Committee. Phenelzine. British National Formulary [online]. London. BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 17/10/2017. Link Pharmaceuticals Ltd. Nardil 15 mg Film-coated Tablet data sheet 28 April 2017. Medsafe. http://www.medsafe.govt.nz/. Accessed 17/10/2017. McEvoy GK, Snow EK, Miller J et al (eds). Phenelzine Sulfate. AHFS Drug Information (AHFS DI) [online]. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP). https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 17/10/2017. Phenelzine Sulfate Tablet (Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.). DailyMed. Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/. Accessed 17/10/2017.
|