Peripheral vascular disease
Adult: As extended-release tab: 400 mg tid, may be reduced to 400 mg bid according to toxicity.
|
Indications and Dosage
Oral
Peripheral vascular disease Adult: As extended-release tab: 400 mg tid, may be reduced to 400 mg bid according to toxicity.
|
||||
|
Renal Impairment
|
||||
|
Hepatic Impairment
Severe: Dose reduction may be necessary.
|
||||
|
Administration
Should be taken with food.
|
||||
|
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to pentoxifylline, other methyl xanthines. Cerebral and extensive retinal haemorrhage, acute MI, severe cardiac arrhythmias.
|
||||
|
Special Precautions
Patient w/ risk factors complicated by haemorrhage (e.g. recent surgery, peptic ulceration, cerebral and/or retinal bleeding), cerebrovascular disease, hypotension, severe coronary artery disease. Renal and severe hepatic impairment. Pregnancy and lactation.
|
||||
|
Adverse Reactions
Significant: Anaphylactic reaction, angina, transient hypotension, reduction in coronary artery perfusion, arrhythmia.
Nervous: Headache, dizziness, tremor, nervousness, drowsiness, insomnia, agitation, sleep disorder. CV: Tachycardia, flushing. GI: Nausea, vomiting, epigastric discomfort, abdominal distention, constipation, diarrhoea, dyspepsia, hypersalivation. Resp: Bronchospasm. Hepatic: Increased transaminases, cholestasis. Haematologic: Thrombocytopenia, leukopenia/neutropenia, haemorrhage. Ophthalmologic: Blurred vision. Dermatologic: Rash, erythema, pruritus, urticaria. |
||||
|
Monitoring Parameters
Monitor prothrombin time, Hb, haematocrit. Monitor renal function.
|
||||
|
Overdosage
Symptoms: Somnolence, loss of consciousness, convulsions, agitation, flushing, hypotension and fever. Management: Symptomatic and supportive treatment. Perform gastric lavage and/or give activated charcoal. Maintain BP and support respiration and control convulsions.
|
||||
|
Drug Interactions
Increased exposure and toxicity w/ cimetidine, ciprofloxacin. Increased risk of bleeding and prolonged prothrombin time w/ anticoagulants (e.g. warfarin), platelet aggregation inhibitors (e.g. clopidogrel), and ketorolac. May increase theophylline levels and toxicity. Increased pharmacological effects of antihypertensive agents, insulin and oral hypoglycaemic agents.
|
||||
|
Action
Description: Pentoxifylline is a xanthine derivative. The exact mechanism of action has not been fully elucidated. But it is thought to decrease blood viscosity, increase leukocyte deformability and erythrocyte flexibility, and decrease neutrophil adhesion/activation. It also improves microcirculation and peripheral tissue oxygenation by increasing blood flow.
Onset: W/in 2-4 wk. Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the GI tract. Time to peak plasma concentration: W/in 2-4 hr. Distribution: Enters breast milk. Metabolism: Undergoes extensive first pass metabolism in the liver. Metabolised in the erythrocyte membrane and liver via reduction and oxidation into active metabolite I [1-(5-hydroxyhexyl)-3,7-dimethylxanthine] and metabolite V [1-(3-carboxypropyl)-3,7-dimethylxanthine] respectively. Excretion: Mainly via urine (95%; 50-80%, as metabolite V, 20%, as other metabolites); faeces (<4%). Plasma elimination half-life: 24-48 min (pentoxifylline); 60-96 min (metabolites). |
||||
|
Chemical Structure
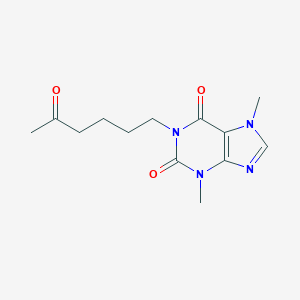 Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Database. Pentoxifylline, CID=4740, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Pentoxifylline (accessed on Jan. 22, 2020) |
||||
|
Storage
Store between 20-25°C. Protect from light.
|
||||
|
ATC Classification
C04AD03 - pentoxifylline ; Belongs to the class of purine derivative agents. Used as peripheral vasodilators.
|
||||
|
References
Anon. Pentoxifylline. Lexicomp Online. Hudson, Ohio. Wolters Kluwer Clinical Drug Information, Inc. https://online.lexi.com. Accessed 10/10/2017. Buckingham R (ed). Pentoxifylline. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference [online]. London. Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 10/10/2017. Joint Formulary Committee. Pentoxifylline (Oxypentifylline). British National Formulary [online]. London. BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 10/10/2017. McEvoy GK, Snow EK, Miller J et al (eds). Pentoxifylline. AHFS Drug Information (AHFS DI) [online]. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP). https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 10/10/2017. Pentoxifylline Tablet, Extended Release (PD-Rx Pharmaceuticals, Inc.). DailyMed. Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/. Accessed 10/10/2017.
|