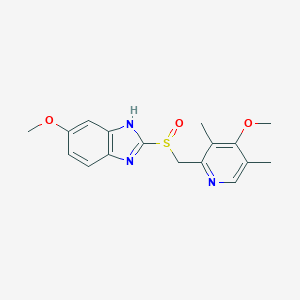
Eradication of H. pylori associated with peptic ulcer disease, Gastric and duodenal ulcers, Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease, NSAID-associated ulceration
Adult: 40 mg once daily given via infusion over 20-30 minutes until oral administration is possible.
Intravenous
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
Adult: Initially, 60 mg daily via infusion over 20-30 minutes, adjust dose according to response. Daily doses >60 mg should be given in 2 divided doses.
Oral
NSAID-associated ulceration
Adult: 20 mg once daily for up to 8 weeks. Maintenance: 20 mg once daily.
Oral
Eradication of H. pylori associated with peptic ulcer disease
Adult: 20 mg bid for 1 week in combination with clarithromycin and with either amoxicillin or metronidazole. Alternatively, 40 mg once daily for 1 week in combination with amoxicillin and metronidazole.
Child: >4 years 15-30 kg: 10 mg bid. 31->40 kg: 20 mg bid. All doses are given in combination with amoxicillin and clarithromycin for 1 week.
Child: >4 years 15-30 kg: 10 mg bid. 31->40 kg: 20 mg bid. All doses are given in combination with amoxicillin and clarithromycin for 1 week.
Oral
Peptic ulcer
Adult: 20 mg or 40 mg once daily. Treatment duration: 4 weeks (duodenal ulcer); 8 weeks (gastric ulcer). Maintenance: 10-20 mg once daily, may increase up to 40 mg according to response.
Oral
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease
Adult: 20 mg once daily for 4-8 weeks. For severe case: 40 mg once daily for 8 weeks. Maintenance: 10 mg once daily, may increase to 20-40 mg once daily if necessary.
Child: ≥1 year weighing 10-20 kg: 10 mg once daily, increased to 20 mg once daily if necessary. ≥2 years weighing >20 kg: 20 mg once daily, increased to 40 mg once daily if necessary. Treatment duration: 4-8 weeks.
Child: ≥1 year weighing 10-20 kg: 10 mg once daily, increased to 20 mg once daily if necessary. ≥2 years weighing >20 kg: 20 mg once daily, increased to 40 mg once daily if necessary. Treatment duration: 4-8 weeks.
Oral
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
Adult: Initially, 60 mg daily, adjust as required. Usual dose: 20-120 mg daily. Dose >80 mg should be given in 2 divided doses.




 Sign Out
Sign Out