Fibromyalgia
Adult: Initially, 12.5 mg as a single dose on day 1, then 12.5 mg bid on days 2-3, then 25 mg bid on days 4-7, and 50 mg bid thereafter. Doses may be increased to 100 mg bid according to individual response.
|
Indications and Dosage
Oral
Fibromyalgia Adult: Initially, 12.5 mg as a single dose on day 1, then 12.5 mg bid on days 2-3, then 25 mg bid on days 4-7, and 50 mg bid thereafter. Doses may be increased to 100 mg bid according to individual response.
|
||||
|
Renal Impairment
ESRD: Not recommended.
|
||||
|
Administration
Should be taken with food. Preferably taken during meals.
|
||||
|
Contraindications
Severe cardiac function impairment or very high risk of serious cardiac arrhythmia (e.g. significant left ventricular dysfunction, NYHA Class III/IV), uncontrolled hypertension, severe or unstable coronary heart disease, uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma. Use with MAOIs (intended to treat psychiatric disorders) either concurrently, or within 14 days of discontinuing MAOIs, or within 5 days of discontinuing milnacipran. Treatment initiation in patients receiving linezolid or IV methylene blue.
|
||||
|
Special Precautions
Patients with major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder or other psychiatric disorders, seizure disorders or conditions predisposing to seizures (e.g. brain damage, alcoholism), high intra-ocular pressure or at risk of narrow-angle glaucoma, previous bleeding abnormalities, pre-existing hypertension, tachyarrhythmias (e.g. atrial fibrillation) or other CV disease, volume depletion, substantial alcohol use or evidence of chronic liver disease, history of dysuria (especially in males with prostatic hypertrophy, prostatitis, or other lower urinary tract disorders). Avoid abrupt withdrawal. Severe hepatic and moderate to severe renal impairment including ESRD. Elderly. Pregnancy and lactation.
|
||||
|
Adverse Reactions
Significant: Suicidal thinking and behaviour, worsening of depression, activation of mania or hypomania, abnormal bleeding events, CV effects (e.g. increase blood pressure and heart rate), bone fractures, hepatotoxicity (e.g. increased liver enzymes, severe liver injury including fulminant hepatitis), ocular effects (e.g. pupillary dilation, episodes of narrow-angle glaucoma), genitourinary effects (e.g. urinary hesitancy or retention, dysuria), syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH), hyponatraemia, seizures, withdrawal symptoms.
Cardiac disorders: Palpitation, tachycardia, chest pain. Eye disorders: Blurred vision. Gastrointestinal disorders: Nausea, constipation, vomiting, dry mouth, abdominal pain, diarrhoea. General disorders and admin site conditions: Chills, fever, fatigue, irritability, peripheral oedema. Infections and infestations: Upper respiratory tract infection, UTI. Investigations: Decreased urine output, weight decreased or increased. Metabolism and nutrition disorders: Decreased appetite, hypercholesterolaemia. Nervous system disorders: Headache, dizziness, migraine, tremor, somnolence. Psychiatric disorders: Insomnia, anxiety, depression, stress. Renal and urinary disorders: Urethral pain, cystitis. Reproductive system and breast disorders: Erectile dysfunction, ejaculation disorder, testicular pain, libido decreased. Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Dyspnoea. Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Hyperhidrosis, rash, pruritus, night sweats. Vascular disorders: Hot flush, hypertension, flushing. Potentially Fatal: Serotonin syndrome, haemorrhage. |
||||
|
PO: C, Z (Risk of postpartum haemorrhage, persistent pulmonary hypertension in infant and neonatal withdrawal/toxicity in late pregnancy use. Monitor closely.)
|
||||
|
Patient Counseling Information
This drug may diminish mental and physical capacities to perform certain tasks. If affected, do not drive or operate machinery.
|
||||
|
Monitoring Parameters
Monitor blood pressure and heart rate prior to initiating therapy and periodically during treatment; renal function, intraocular pressure (in patients with baseline elevations or history of glaucoma). Closely monitor mental status for signs and symptoms of suicidal ideation (e.g. anxiety, depression, unusual behavioural changes, clinical worsening) especially at the start of therapy or when doses are increased or decreased.
|
||||
|
Overdosage
Symptoms: Increased blood pressure, dizziness, confusional state, increased hepatic enzymes, changes in the level of consciousness (ranging from somnolence to coma), cardiorespiratory arrest. Management: Symptomatic and supportive treatment. May consider gastric lavage and activated charcoal administration soon after ingestion. Maintain adequate airway, oxygenation, and ventilation. May administer cyproheptadine with adequate temperature control to treat serotonin syndrome.
|
||||
|
Drug Interactions
Increased risk of bleeding with aspirin, NSAIDs, warfarin, and other anticoagulants. May increase risk of hyponatraemia with diuretics. May inhibit antihypertensive effect of clonidine. May potentiate adverse haemodynamic effects with digoxin. May increase risk of paroxysmal hypertension and cardiac arrhythmias with epinephrine or norepinephrine.
Potentially Fatal: Increased risk of serotonin syndrome or neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS)-like reactions with serotonergic agents (e.g. SSRIs, triptans, TCAs, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, buspirone, tryptophan), agents which impair metabolism of serotonin (e.g. MAOIs for treatment of psychiatric disorders, linezolid, IV methylene blue), and with antipsychotics or other dopamine antagonists. |
||||
|
Food Interaction
Increased risk of serotonin syndrome with St. John’s wort. Increased risk of psychomotor impairment and hepatotoxicity with alcohol.
|
||||
|
Action
Description: Milnacipran is a potent inhibitor of neuronal norepinephrine and serotonin reuptake. It inhibits norepinephrine uptake with approx 3-fold higher potency than serotonin in vitro without directly affecting the uptake of dopamine or other neurotransmitters.
Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Bioavailability: Approx 85-90%. Time to peak plasma concentration: 2-4 hours. Distribution: Enters breast milk. Plasma protein binding: 13%. Metabolism: Metabolised in the liver mainly via glucuronide conjugation and to a lesser extent via N-dealkylation to inactive metabolites. Excretion: Via urine (approx 55% as unchanged drug). Elimination half-life: 6-8 hours. |
||||
|
Chemical Structure
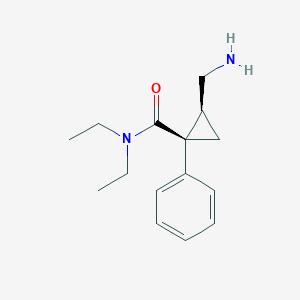 Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Database. Milnacipran, CID=65833, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Milnacipran (accessed on Jan. 22, 2020) |
||||
|
Storage
Store at 25°C.
|
||||
|
MIMS Class
|
||||
|
ATC Classification
N06AX17 - milnacipran ; Belongs to the class of other antidepressants.
|
||||
|
References
Anon. Milnacipran. AHFS Clinical Drug Information [online]. Bethesda, MD. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. https://www.ahfscdi.com. Accessed 14/08/2019. Anon. Milnacipran. Lexicomp Online. Hudson, Ohio. Wolters Kluwer Clinical Drug Information, Inc. https://online.lexi.com. Accessed 14/08/2019. Buckingham R (ed). Milnacipran Hydrochloride. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference [online]. London. Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 14/08/2019. Savella Tablet, Film Coated (Allergan, Inc.). DailyMed. Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/. Accessed 14/08/2019. Savella Tablets (Forest Laboratories, Inc.). U.S. FDA. https://www.fda.gov/. Accessed 14/08/2019.
|