Short-term management of anxiety
Adult: 400 mg 3-4 times a day. Max: 2,400 mg daily.
Elderly: Up to 200 mg 3-4 times a day.
Elderly: Up to 200 mg 3-4 times a day.
|
Indications and Dosage
Oral
Short-term management of anxiety Adult: 400 mg 3-4 times a day. Max: 2,400 mg daily.
Elderly: Up to 200 mg 3-4 times a day. |
|
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity. Drug dependence (e.g. alcohol). Acute intermittent porphyria, acute pulmonary insufficiency, resp depression. Pregnancy and lactation.
|
|
Special Precautions
Patient w/ suicidal ideation, depression, seizure disorders (e.g. epilepsy), history of drug abuse or acute alcoholism, resp disease or muscle weakness. Avoid abrupt withdrawal. Renal and hepatic impairment. Elderly or debilitated patients.
|
|
Adverse Reactions
Significant: Dependence, hypersensitivity reactions (e.g. skin rashes; rarely, anaphylaxis, angioedema, bronchospasm, exfoliative dermatitis, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome).
Nervous: Drowsiness, dizziness, overstimulation, euphoria, slurred speech, vertigo, headache, paradoxical excitement, paraesthesia, ataxia. CV: Hypotension, arrhythmia, tachycardia, palpitation, transient ECG changes, syncope, peripheral oedema. GI: Transient nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, stomatitis, proctitis, anorexia. Genitourinary: Anuria, oliguria. Ophthalmologic: Visual disturbances. Others: Chills, fever. Potentially Fatal: Withdrawal symptoms (e.g. delirium tremens, tremors, muscle twitching, insomnia, confusion; rarely, convulsions); rarely, hypertensive crisis, bullous dermatitis, agranulocytosis, aplastic anaemia, thrombocytopenic purpura. |
|
Patient Counseling Information
This drug may cause drowsiness or dizziness, if affected, do not drive or operate machinery.
|
|
Monitoring Parameters
Monitor for anxiety symptoms, mental status, CNS depression, drug abuse, overuse, tolerance and dependence. Assess for history of addiction.
|
|
Overdosage
Symptoms: Drowsiness, lethargy, stupor, ataxia, coma, shock, vasomotor and resp collapse. Management: Supportive and symptomatic treatment. Maintain adequate airway, assisted respiration, and cautious admin of vasopressor agents if indicated. May perform gastric lavage in comatose, having seizure or lacks gag reflex patient if an inflated endotracheal tube cuff is inserted or induce emesis if patient is conscious. Admin of activated charcoal after gastric lavage/emesis for complete gastric emptying. Forced diuresis w/ an osmotic diuretic (e.g. mannitol) or peritoneal dialysis may be beneficial. Monitor urinary output and avoid overhydration.
|
|
Drug Interactions
Increased sedative effects w/ CNS depressants and psychotropic agents.
|
|
Food Interaction
Additive sedative effect w/ alcohol.
|
|
Lab Interference
Falsely high urinary 17-ketosteroid and 17-ketogenicsteroid concentration in Zimmerman reaction and 17-hydroxycorticosteroid concentration in modified Glenn-Nelson technique.
|
|
Action
Description: Meprobamate is a carbamate derivative w/ CNS depressant action similar to barbiturates. The exact mechanism of action is still unknown. It acts in the thalamus and limbic system, and appears to inhibit multineuronal spinal reflexes. It also has hypnotic, sedative and some muscle relaxant properties.
Onset: Sedation: Approx 1 hr. Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Readily absorbed from the GI tract. Time to peak plasma concentration: 1-3 hr. Distribution: Widely distributed. Crosses placenta and enters breast milk. Plasma protein binding: Approx 20%. Metabolism: Extensively metabolised in the liver. Excretion: Mainly via urine (8-20% as unchanged drug); faeces (10% as metabolites). Elimination half-life: 6-17 hr. |
|
Chemical Structure
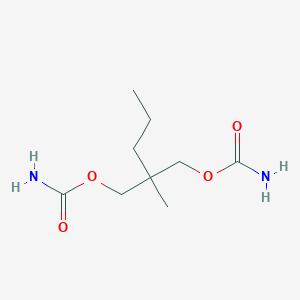 Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Database. Meprobamate, CID=4064, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Meprobamate (accessed on Jan. 22, 2020) |
|
Storage
Store at 25°C.
|
|
MIMS Class
|
|
ATC Classification
N05BC01 - meprobamate ; Belongs to the class of carbamates anxiolytics. Used in the management of anxiety, agitation or tension.
|
|
References
Anon. Meprobamate. Lexicomp Online. Hudson, Ohio. Wolters Kluwer Clinical Drug Information, Inc. https://online.lexi.com. Accessed 24/07/2017. Buckingham R (ed). Meprobamate. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference [online]. London. Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 24/07/2017. Joint Formulary Committee. Meprobamate. British National Formulary [online]. London. BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 24/07/2017. McEvoy GK, Snow EK, Miller J et al (eds). Meprobamate. AHFS Drug Information (AHFS DI) [online]. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP). https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 24/07/2017. Meprobamate Tablets USP 200 mg 400 mg (Alembic Pharmaceuticals Limited). DailyMed. Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/. Accessed 24/07/2017.
|