Pulmonary multidrug-resistant tuberculosis
Adult: 100 mg bid for 24 weeks, in combination with other drugs.
|
Indications and Dosage
Oral
Pulmonary multidrug-resistant tuberculosis Adult: 100 mg bid for 24 weeks, in combination with other drugs.
|
|
Administration
film-coated tab: Should be taken with food.
|
|
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity. Serum albumin <2.8 g/dL. Concomitant use with strong CYP3A4 inducers.
|
|
Special Precautions
Patient with risk factors for QT prolongation (e.g. electrolyte imbalance, MI, severe hypertension, left ventricular hypertrophy, hypoalbuminaemia). Moderate to severe hepatic or severe renal impairment. Pregnancy and lactation.
|
|
Adverse Reactions
Significant: QT interval prolongation.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: Reticulocytosis, haemoptysis. Cardiac disorders: Palpitations, chest pain. Ear and labyrinth disorders: Tinnitus, ear pain. Endocrine disorders: Hyperlipidaemia. Eye disorders: Photophobia. Gastrointestinal disorders: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, oropharyngeal pain. General disorders and administration site conditions: Malaise, asthenia. Investigations: Hypokalaemia. Metabolism and nutrition disorders: Decreased appetite. Nervous system disorders: Headache, paraesthesia, dizziness, tremor, peripheral neuropathy, hypoaesthesia, restlessness. Psychiatric disorders: Insomnia, agitation, anxiety, depression. Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Dyspnoea. Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Dermatitis, hyperhidrosis. Vascular disorders: Hypertension, hypotension. |
|
Patient Counseling Information
This drug may cause headache or tremors, if affected, do not drive or operate machinery.
|
|
Monitoring Parameters
Monitor serum albumin, electrolytes and obtain ECG prior initiation and during therapy.
|
|
Drug Interactions
Increased risk of QT interval prolongation with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g. ritonavir, lopinavir), certain antimicrobials (e.g. clarithromycin, erythromycin, moxifloxacin), neuroleptics (e.g. phenothiazines, haloperidol), antiarrhythmics (e.g. amiodarone, quinidine), certain non-sedating antihistamines (e.g. terfenadine, astemizole), cisapride, droperidol, domperidone, methadone.
Potentially Fatal: Significantly reduced exposure with strong CYP3A4 inducers (e.g. carbamazepine). |
|
Food Interaction
Increased bioavailability with food.
|
|
Action
Description: Delamanid is a nitroimidazo-oxazole antimycobacterial prodrug that is activated through bioreduction of its nitro group by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It inhibits the synthesis of mycobacterial cell wall components, methoxymycolic and ketomycolic acids.
Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Increased bioavailability with food. Distribution: Widely distributed throughout the body. Plasma protein binding: ≥99.5%. Metabolism: Metabolised mainly in plasma by albumin and to a lesser extent via hydroxylation and oxidation by CYP3A4 enzymes to form DM-6705. Excretion: Mainly via faeces. Elimination half-life: Approx 30-38 hours. |
|
Chemical Structure
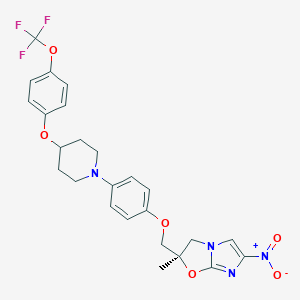 Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Database. Delamanid, CID=6480466, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Delamanid (accessed on Jan. 20, 2020) |
|
Storage
Protect from moisture.
|
|
MIMS Class
|
|
ATC Classification
J04AK06 - delamanid ; Belongs to the class of other drugs used in the systemic treatment of tuberculosis.
|
|
References
Buckingham R (ed). Delamanid. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference [online]. London. Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 07/03/2018. Deltyba 50 mg Film-Coated Tablets (Otsuka Novel Products GmbH). European Medicines Agency [online]. Accessed 16/03/2018. Joint Formulary Committee. Delamanid. British National Formulary [online]. London. BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 07/03/2018.
|