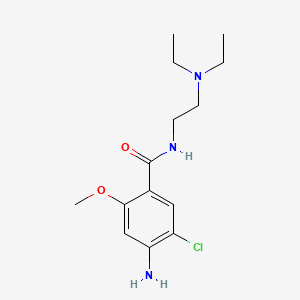
Diabetic gastric stasis
Adult: Severe cases: 10 mg via slow IV inj over 1-2 minutes or IM inj up to 10 days and may shift to oral therapy once possible. Treatment and dosing recommendations may vary among individual products and between countries (refer to specific product guidelines).
Intramuscular, Intravenous
Prophylaxis of postoperative nausea and vomiting
Adult: 10 mg as a single dose via slow IV inj over at least 3 minutes or IM inj. Treatment and dosage recommendations may vary among individual products and between countries (refer to specific product guidelines).
Elderly: Dose reduction may be needed.
Elderly: Dose reduction may be needed.
Intramuscular, Intravenous
Nausea and vomiting, Prophylaxis of nausea and vomiting associated with radiation therapy
Adult: 10 mg up to tid via slow IV inj over at least 3 minutes or IM inj. Max: 30 mg daily or 0.5 mg/kg daily. Dosing interval: ≥6 hours. Treatment and dosing recommendations may vary among individual products and between countries (refer to specific product guidelines).
Elderly: Dose reduction may be needed.
Elderly: Dose reduction may be needed.
Intravenous
Prophylaxis of delayed chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting
Child: As a 2nd-line option: 1-<3 years 10-14 kg: 1 mg; 3-<5 years 15-19 kg: 2 mg; 5-<9 years 20-29 kg: 2.5 mg; 9-18 years 30-60 kg: 5 mg; 15-18 years >60 kg: 10 mg. All doses to be given up to tid and via slow IV push over at least 3 minutes. Dosing interval: ≥6 hours. Max: 0.5 mg/kg in 24 hours. Max treatment duration: 5 days. Treatment and dosing recommendations may vary among individual products and between countries (refer to specific product guidelines).
Intravenous
Prophylaxis of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting
Adult: Loading dose: 2-4 mg/kg via continuous infusion over 15-20 minutes, given before cancer therapy. Maintenance: 3-5 mg/kg via continuous infusion over 8-12 hours. Alternatively, initial dose of up to 2 mg/kg via intermittent infusion over at least 15 minutes, may be given before cancer therapy and repeated at 2-hourly intervals. Max total dose: 10 mg/kg in 24 hours. Treatment and dosing recommendations may vary among individual products and between countries (refer to specific product guidelines).
Elderly: Dose reduction may be needed.
Elderly: Dose reduction may be needed.
Intravenous
Postoperative nausea and vomiting
Child: As a 2nd-line option: 1-<3 years 10-14 kg: 1 mg; 3-<5 years 15-19 kg: 2 mg; 5-<9 years 20-29 kg: 2.5 mg; 9-18 years 30-60 kg: 5 mg; 15-18 years >60 kg: 10 mg. All doses to be given up to tid and via slow IV push over at least 3 minutes. Dosing interval: ≥6 hours. Max: 0.5 mg/kg in 24 hours. Max treatment duration: 48 hours. Treatment and dosing recommendations may vary among individual products and between countries (refer to specific product guidelines).
Intravenous
Intubation of the small intestine, Premedication for radiologic examination of the upper gastrointestinal tract
Adult: 10 mg as a single dose, given over 1-2 minutes. Treatment and dosing recommendations may vary among individual products and between countries (refer to specific product guidelines).
Child: <6 years 0.1 mg/kg; 6-14 years 2.5-5 mg; >14 years Same as adult dose. All doses to be given as a single dose over 1-2 minutes. Treatment and dosing recommendations may vary among individual products and between countries (refer to specific product guidelines).
Child: <6 years 0.1 mg/kg; 6-14 years 2.5-5 mg; >14 years Same as adult dose. All doses to be given as a single dose over 1-2 minutes. Treatment and dosing recommendations may vary among individual products and between countries (refer to specific product guidelines).
Nasal
Diabetic gastric stasis
Adult: 1 spray (15 mg) in 1 nostril 4 times daily (30 minutes before each meal and at bedtime) for 2-8 weeks according to symptomatic response. Max: 4 sprays (60 mg) daily. Treatment recommendations may vary among individual products and between countries (refer to specific product guidelines).
Elderly: ≥65 years Not recommended for initial therapy.
Elderly: ≥65 years Not recommended for initial therapy.
Oral
Nausea and vomiting, Prophylaxis of nausea and vomiting associated with radiation therapy
Adult: 10 mg up to tid. Max: 30 mg daily or 0.5 mg/kg daily. Max treatment duration: 5 days. Dosing interval: ≥6 hours. Treatment and dosing recommendations may vary among individual products and between countries (refer to specific product guidelines).
Elderly: Dose reduction may be needed.
Elderly: Dose reduction may be needed.
Oral
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease
Adult: In patients who fail to respond to conventional therapy: 10-15 mg 4 times daily given 30 minutes before each meal and at bedtime for 4-12 weeks, depending on endoscopic response. Max: 60 mg daily. If the occurrence of symptoms is intermittent or at specific times of the day, doses up to 20 mg may be given as a single dose prior to provoking situation. Treatment and dosing recommendations may vary among individual products and between countries (refer to specific product guidelines).
Elderly: Initially, 5 mg 4 times daily given 30 minutes before each meal and at bedtime, then titrate to 10-15 mg 4 times daily according to response and tolerability. Max: 60 mg daily.
Elderly: Initially, 5 mg 4 times daily given 30 minutes before each meal and at bedtime, then titrate to 10-15 mg 4 times daily according to response and tolerability. Max: 60 mg daily.
Oral
Diabetic gastric stasis
Adult: For acute and recurrent cases: 10 mg 4 times daily given 30 minutes before each meal and at bedtime for 2-8 weeks according to response. Max: 40 mg daily. Treatment and dosing recommendations may vary among individual products and between countries (refer to specific product guidelines).
Elderly: Initially, 5 mg 4 times daily given 30 minutes before each meal and at bedtime, then titrate to 10 mg 4 times daily according to response and tolerability. Max: 40 mg daily.
Elderly: Initially, 5 mg 4 times daily given 30 minutes before each meal and at bedtime, then titrate to 10 mg 4 times daily according to response and tolerability. Max: 40 mg daily.
Oral
Prophylaxis of delayed chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting
Adult: 10 mg up to tid. Max: 30 mg daily or 0.5 mg/kg daily. Max treatment duration: 5 days. Dosing interval: ≥6 hours. Treatment and dosing recommendations may vary among individual products and between countries (refer to specific product guidelines).
Elderly: Dose reduction may be needed.
Child: As a 2nd-line option: 1-<3 years 10-14 kg: 1 mg; 3-<5 years 15-19 kg: 2 mg; 5-<9 years 20-29 kg: 2.5 mg; 9-18 years 30-60 kg: 5 mg; 15-18 years >60 kg: Same as adult dose. All doses to be given up to tid. Dosing interval: ≥6 hours. Max: 0.5 mg/kg in 24 hours. Max treatment duration: 5 days. Treatment and dosing recommendations may vary among individual products and between countries (refer to specific product guidelines).
Elderly: Dose reduction may be needed.
Child: As a 2nd-line option: 1-<3 years 10-14 kg: 1 mg; 3-<5 years 15-19 kg: 2 mg; 5-<9 years 20-29 kg: 2.5 mg; 9-18 years 30-60 kg: 5 mg; 15-18 years >60 kg: Same as adult dose. All doses to be given up to tid. Dosing interval: ≥6 hours. Max: 0.5 mg/kg in 24 hours. Max treatment duration: 5 days. Treatment and dosing recommendations may vary among individual products and between countries (refer to specific product guidelines).
Oral
Intubation of the small intestine, Premedication for radiologic examination of the upper gastrointestinal tract
Adult: 10-20 mg as a single dose given 5-10 minutes before examination. Treatment and dosing recommendations may vary among individual products and between countries (refer to specific product guidelines).
Child: 15-19 years 10 mg as a single dose given 5-10 minutes before examination.
Child: 15-19 years 10 mg as a single dose given 5-10 minutes before examination.




 Sign Out
Sign Out