Moderate dementia in Alzheimer's disease, Severe dementia in Alzheimer's disease
Adult: Initially, 5 mg once daily for the 1st wk, increased in wkly increments of 5 mg. Max: 20 mg daily.
|
Indications and Dosage
Oral
Moderate dementia in Alzheimer's disease, Severe dementia in Alzheimer's disease Adult: Initially, 5 mg once daily for the 1st wk, increased in wkly increments of 5 mg. Max: 20 mg daily.
|
||||||
|
Renal Impairment
|
||||||
|
Administration
May be taken with or without food.
|
||||||
|
Special Precautions
Patient w/ CV disease, epilepsy, history of convulsions or those w/ predisposing factors for epilepsy. Conditions that may increase urinary pH (e.g. drastic dietary changes). Moderate to severe renal and severe hepatic impairment. Pregnancy and lactation.
|
||||||
|
Adverse Reactions
Headache, dizziness, constipation, HTN, somnolence, anxiety, confusion, hallucinations, fatigue, abnormal gait, hypertonia, vomiting, fungal infections, cystitis, thromboembolism, increased libido, psychotic reactions, pancreatitis; agranulocytosis, leucopenia (including neutropenia), thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, CHF, hepatitis, suicidal ideation, acute renal failure (including increased creatinine and renal impairment), Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
|
||||||
|
Patient Counseling Information
May impair ability to drive or operate machinery.
|
||||||
|
Monitoring Parameters
Monitor cognitive function; periodic ophth examination.
|
||||||
|
Overdosage
Symptoms: Agitation, asthenia, bradycardia, vomiting, dizziness, vertigo, ECG changes, increased BP, visual hallucinations, confusion, lethargy, restlessness, slowed movement, somnolence, stupor, unsteady gait, weakness, loss of consciousness, psychosis, coma. Management: Symptomatic and supportive treatment. May increase elimination by urinary acidification.
|
||||||
|
Drug Interactions
Increased risk of adverse effects w/ amantadine, ketamine or dextromethorphan. May decrease the effects of barbiturates and neuroleptics. May increase the effects of L-dopa, dopaminergic agonists and anticholinergics. May alter the effect of antispasmodics (e.g. dantrolene, or baclofen). Decreased clearance w/ carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and Na bicarbonate. May potentially increase plasma levels of cimetidine, procainamide, ranitidine, quinidine, quinine, nicotine. May decrease serum level of hydrochlorothiazide.
|
||||||
|
Action
Description:
Mechanism of Action: Memantine, a derivative of amantadine, is a noncompetitive N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-receptor antagonist which binds preferentially to NMDA-receptor-operated cation channels. It blocks the action of glutamate, the principal excitatory neurotransmitter in the CNS. Glutamate may contribute to the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease by overstimulating various glutamate receptors resulting in excitotoxicity and neuronal cell death. Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Well absorbed. Absolute bioavailability: Approx 100%. Time to peak plasma concentration: Approx 3-8 hr. Distribution: Volume of distribution: 9-11 L/kg. Plasma protein binding: Approx 45%. Metabolism: Undergoes partial hepatic metabolism to main metabolites including N-3,5-dimethyl-gludantan and 1-nitroso-3,5-dimethyl-adamantane. Excretion: Mainly via urine (approx 57-82% as unchanged drug). Terminal half-life: 60-100 hr. |
||||||
|
Chemical Structure
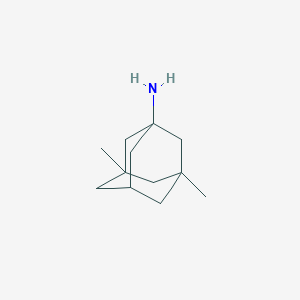 Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Database. Memantine, CID=4054, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Memantine (accessed on Jan. 22, 2020) |
||||||
|
Storage
Store between 20-25°C.
|
||||||
|
MIMS Class
|
||||||
|
ATC Classification
N06DX01 - memantine ; Belongs to the class of other anti-dementia drugs.
|
||||||
|
References
Anon. Memantine. Lexicomp Online. Hudson, Ohio. Wolters Kluwer Clinical Drug Information, Inc. https://online.lexi.com. Accessed 03/12/2015. Buckingham R (ed). Memantine Hydrochloride. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference [online]. London. Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 03/12/2015. Joint Formulary Committee. Memantine Hydrochloride. British National Formulary [online]. London. BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 03/12/2015. McEvoy GK, Snow EK, Miller J et al (eds). Memantine Hydrochloride. AHFS Drug Information (AHFS DI) [online]. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP). https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 03/12/2015. Memantine Hydrochloride Tablet (Mylan Pharmaceuticals Inc.). DailyMed. Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/. Accessed 03/12/2015. Namenda XR Capsules. U.S. FDA. https://www.fda.gov/. Accessed 03/12/2015.
|