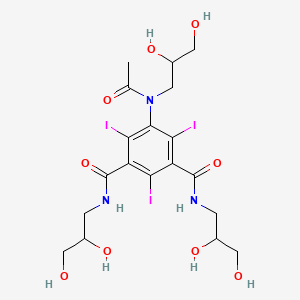
Aortography and selective visceral arteriography
Adult: As 300 mg or 350 mg iodine/mL solution: Aorta (aortic arch and ascending aorta): 50-80 mL; Abdominal aorta and its branches (including coeliac and mesenteric arteries): 30-60 mL; Renal artery: 5-15 mL. Doses may be repeated if required. Max total volume: 290 mL (as 300 mg iodine/mL solution); 250 mL (as 350 mg iodine/mL solution). Aortic root and arch study when used alone: As 350 mg iodine/mL solution: 50 mL (dose range: 20-75 mL). Dosage recommendations may vary among countries or individual products. Refer to specific product guidelines.
Child: Aortic root or arch, descending aorta: As 350 mg iodine/mL solution: 1 mL/kg, may be repeated as needed. Max: 5 mL/kg, up to total volume of 250 mL. Dosage recommendations may vary among countries or individual products. Refer to specific product guidelines.
Child: Aortic root or arch, descending aorta: As 350 mg iodine/mL solution: 1 mL/kg, may be repeated as needed. Max: 5 mL/kg, up to total volume of 250 mL. Dosage recommendations may vary among countries or individual products. Refer to specific product guidelines.
Intra-arterial
Cerebral arteriography
Adult: As 300 mg iodine/mL solution: Common carotid artery: 6-12 mL. Internal carotid artery: 8-10 mL. External carotid artery: 6-9 mL. Vertebral artery: 6-10 mL. Dosage recommendations may vary among countries or individual products. Refer to specific product guidelines.
Intra-arterial
Peripheral arteriography
Adult: Aortofemoral runoffs: As 300 mg iodine/mL solution: 30-90 mL; As 350 mg iodine/mL solution: 20-70 mL. Selective arteriograms: As 300 mg iodine/mL solution: 10-60 mL; As 350 mg iodine/mL solution: 10-30 mL. Dosage recommendations may vary among countries or individual products. Refer to specific product guidelines.
Intra-arterial
Digital subtraction angiography
Adult: As 140 mg iodine/mL solution: Aorta: 20-45 mL at 8-20 mL/second. Carotid artery: 5-10 mL at 3-6 mL/second. Femoral artery: 9-20 mL at 3-6 mL/second. Vertebral artery: 4-10 mL at 2-8 mL/second. Renal artery: 6-12 mL at 3-6 mL/second. Other branches of aorta (including subclavian, axillary, innominate and iliac): 8-25 mL at 3-10 mL/second. Dosage recommendations and concentrations used may vary among countries or individual products. Refer to specific product guidelines.
Intra-arterial
Angiocardiography
Adult: Ventriculography: As 350 mg iodine/mL solution: 40 mL (dose range: 30-60 mL) as a single dose, may be repeated as needed. Max volume with multiple inj: 250 mL. May be combined with selective coronary arteriography. Selective coronary arteriography: As 350 mg iodine/mL solution: 4-8 mL per inj; alternatively, 5 mL (dose range: 3-14 mL) per inj, may be repeated as necessary. Max volume with multiple inj: 250 mL. Dosage recommendations may vary among countries or individual products. Refer to specific product guidelines.
Child: Ventriculography: As 300 mg iodine/mL solution: 1.75 mL/kg (dose range: 1.5-2 mL/kg), may be repeated as needed. Max dose with multiple inj: 5 mL/kg, up to a total volume of 291 mL. As 350 mg iodine/mL solution: 1.25 mL/kg (dose range: 1-1.5 mL/kg), may be repeated as necessary. Max dose with multiple inj: 5 mL/kg, up to a total volume of 250 mL. Pulmonary angiography: As 300 mg iodine/mL solution: 1 ml/kg. Dosage may vary among countries or individual products. Refer to specific product guidelines.
Child: Ventriculography: As 300 mg iodine/mL solution: 1.75 mL/kg (dose range: 1.5-2 mL/kg), may be repeated as needed. Max dose with multiple inj: 5 mL/kg, up to a total volume of 291 mL. As 350 mg iodine/mL solution: 1.25 mL/kg (dose range: 1-1.5 mL/kg), may be repeated as necessary. Max dose with multiple inj: 5 mL/kg, up to a total volume of 250 mL. Pulmonary angiography: As 300 mg iodine/mL solution: 1 ml/kg. Dosage may vary among countries or individual products. Refer to specific product guidelines.
Intra-articular, Intrasynovial
Arthrography
Adult: Knee joint: As 240 mg or 300 mg iodine/mL solution: 5-15 mL; As 350 mg iodine/mL solution: 5-10 mL. Shoulder joint: As 240 mg iodine/mL solution: 3 mL; As 300 mg iodine/mL solution: 10 mL. Temporomandibular joint: As 300 mg iodine/mL solution: 0.5-1 mL. Higher volumes are recommended for single-contrast examinations; lower volumes are recommended for double-contrast examinations. Use active or passive manipulation to disperse the media throughout the joint space.
Intracavitary
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), Endoscopic retrograde pancreatography (ERP)
Adult: As 240 mg iodine/mL solution (undiluted): 10-50 mL. Dosage recommendations may vary among countries or individual products. Refer to specific product guidelines.
Intracavitary, Intraperitoneal, Intrauterine
Hysterosalpingography
Adult: As 240 mg iodine/mL solution (undiluted): 15-50 mL or 15-20 mL. As 300 mg iodine/mL solution (undiluted): 15-25 mL or 15-20 mL. Dosage recommendations may vary among countries or individual products. Refer to specific product guidelines.
Intracavitary, Intraperitoneal
Herniography
Adult: As 240 mg iodine/mL solution (undiluted): 50 mL. Doses are administered into the body cavity. Dosage may vary based on individual anatomy and/or disease state.
Intracavitary, Urethral
Voiding cystourethrography
Child: As 240 mg, 300 mg or 350 mg iodine/mL solution (diluted with sterile water for inj to prepare 50-100 mg iodine/mL concentration): Usual volume range: 50-300 mL (at 100 mg iodine/mL concentration); 50-600 mL (at 50 mg iodine/mL concentration).
Intracavitary
Sialography
Adult: As 240 mg or 300 mg iodine/mL solution: 0.5-2 mL.
Intrathecal
Myelography
Adult: Lumbar (via lumbar inj): As 180 mg iodine/mL solution: 10-17 mL; As 240 mg iodine/mL solution: 7-12.5 mL. Thoracic (via lumbar or cervical inj): As 240 mg iodine/mL solution: 6-12.5 mL; As 300 mg iodine/mL solution: 6-10 mL. Cervical (via lumbar inj): As 240 mg iodine/mL solution: 6-12.5 mL; As 300 mg iodine/mL solution: 6-10 mL. Cervical (via C1-2 inj): As 180 mg iodine/mL solution: 7-10 mL; As 240 mg iodine/mL solution: 6-12.5 mL; As 300 mg iodine/mL solution: 4-10 mL. Total columnar (via lumbar inj): As 240 mg iodine/mL solution: 6-12.5 mL; As 300 mg iodine/mL solution: 6-10 mL. Doses are given via slow inj over 1-2 minutes. For single myelographic procedure: Max total dose of 3,100 mg iodine or 300 mg iodine/mL concentration. If repeat procedures are needed, wait for at least 48 hours (preferably 5-7 days) before repeating the test. Dosage recommendations, concentrations used, and inj administration may vary among countries or individual products. Refer to specific product guidelines.
Child: Lumbar, thoracic, cervical and/or total columnar (via lumbar puncture): As 180 mg iodine/mL solution. 0-<3 months 2-4 mL; 3-<36 months 4-8 mL; 3-<7 years 5-10 mL; 7-<13 years 5-12 mL; 13-18 years 6-15 mL. For single myelographic procedure: Max total dose of 2,700 mg iodine or 180 mg iodine/mL concentration. If repeat procedures are needed, wait for at least 48 hours (preferably 5-7 days) before repeating the test. Dosage recommendations may vary among countries or individual products. Refer to specific product guidelines.
Child: Lumbar, thoracic, cervical and/or total columnar (via lumbar puncture): As 180 mg iodine/mL solution. 0-<3 months 2-4 mL; 3-<36 months 4-8 mL; 3-<7 years 5-10 mL; 7-<13 years 5-12 mL; 13-18 years 6-15 mL. For single myelographic procedure: Max total dose of 2,700 mg iodine or 180 mg iodine/mL concentration. If repeat procedures are needed, wait for at least 48 hours (preferably 5-7 days) before repeating the test. Dosage recommendations may vary among countries or individual products. Refer to specific product guidelines.
Intrathecal
Computed tomographic cisternography
Adult: As 240 mg iodine/mL solution: 4-12 mL via lumbar inj. Dosage recommendations and concentrations used may vary among countries or individual products. Refer to specific product guidelines.
Intravenous
Contrast-enhanced computerised tomography
Adult: Head imaging via rapid inj: As 300 mg iodine/mL solution: 70-150 mL; As 350 mg iodine/mL solution: 80 mL. Head imaging via infusion: As 240 mg iodine/mL solution: 120-250 mL. Body imaging via rapid inj: As 300 mg iodine/mL solution: 50-200 mL; As 350 mg iodine/mL solution: 60-100 mL. Dosage recommendations and concentrations used may vary among countries or individual products. Refer to specific product guidelines.
Child: Head imaging: As 240 mg or 300 mg iodine/mL: 1-2 mL/kg. Max dose may be product dependent. Dosage recommendations may vary among countries or individual products. Refer to specific product guidelines.
Child: Head imaging: As 240 mg or 300 mg iodine/mL: 1-2 mL/kg. Max dose may be product dependent. Dosage recommendations may vary among countries or individual products. Refer to specific product guidelines.
Intravenous
Peripheral venography, Phlebography
Adult: As 240 mg iodine/mL solution: 20-150 mL per leg. As 300 mg iodine/mL solution: 40-100 mL per leg. Dosage recommendations and concentrations used may vary among countries or individual products. Refer to specific product guidelines.
Intravenous
Contrast-enhanced computerised tomography of the abdomen
Adult: In conjunction with orally administered iohexol inj or oral solution: As 300 mg iodine/mL solution (diluted): 100-150 mL. Doses may be given up to 40 minutes after consumption of oral iohexol.
Child: In conjunction with orally administered iohexol inj or oral solution: As 240 mg or 300 mg iodine/mL solution (diluted): 2 mL/kg (dose range: 1-2 mL/kg). Max: 3 mL/kg. Doses may be given up to 60 minutes after consumption of oral iohexol.
Child: In conjunction with orally administered iohexol inj or oral solution: As 240 mg or 300 mg iodine/mL solution (diluted): 2 mL/kg (dose range: 1-2 mL/kg). Max: 3 mL/kg. Doses may be given up to 60 minutes after consumption of oral iohexol.
Intravenous
Digital subtraction angiography
Adult: As 300 mg or 350 mg iodine/mL solution: 20-60 mL per inj. Alternatively for 350 mg iodine/mL solution, may give usual dose of 30-50 mL via pressure injector at a rate of 7.5-30 mL/second. May require 3 or more inj. Max total dose: 250 mL. Dosage recommendations and concentrations used may vary among countries or individual products. Refer to specific product guidelines.
Intravenous
Excretory urography
Adult: As 300 mg or 350 mg iodine/mL solution: 40-80 mL, or 0.6-1.2 mL/kg. Dosage recommendations may vary among countries or individual products. Refer to specific product guidelines.
Child: As 240 mg iodine/mL solution: <7 kg: 4 mL/kg; >7 kg: 3 mL/kg. As 300 mg iodine/mL solution: <7 kg: 3 mL/kg; >7 kg: 2 mL/kg. Alternatively for 300 mg iodine/mL solution, may give usual dose of 1-1.5 mL/kg (dose range: 0.5-3 mL/kg). Max total dose: 3 mL/kg. Dosage recommendations and concentrations used may vary among countries or individual products. Refer to specific product guidelines.
Child: As 240 mg iodine/mL solution: <7 kg: 4 mL/kg; >7 kg: 3 mL/kg. As 300 mg iodine/mL solution: <7 kg: 3 mL/kg; >7 kg: 2 mL/kg. Alternatively for 300 mg iodine/mL solution, may give usual dose of 1-1.5 mL/kg (dose range: 0.5-3 mL/kg). Max total dose: 3 mL/kg. Dosage recommendations and concentrations used may vary among countries or individual products. Refer to specific product guidelines.
Oral
Contrast-enhanced computerised tomography of the abdomen
Adult: As 9 mg iodine/mL powder for oral solution (Oraltag®): 500-1,000 mL given 20-60 minutes prior to image acquisition. If the patient has difficulty in consuming the required volume, a higher concentration of solution (up to 21 mg iodine/mL solution) may be prepared and administered at a smaller volume. Max total iodine dose: 9 g. In conjunction with IV administration of iohexol: As 240 mg, 300 mg or 350 mg iodine/mL (diluted to 6-12 mg iodine/mL concentration): 500-1,000 mL. Use smaller volumes for higher concentrations. As 9 mg and 12 mg iodine/mL oral solution (Omnipaque®): 500-1,000 mL. Doses may be given all at once or over 45 minutes if with difficulty in consumption.
Child: As 9 mg iodine/mL powder for oral solution (Oraltag®): <3 years 120-300 mL. Max total iodine dose: 4.5 g; 3-18 years 280-750 mL. Max total iodine dose: 9 g. Doses are given 20-60 minutes prior to image acquisition and will vary based on the size of the patient. If the patient has difficulty in consuming the required volume, a higher concentration of solution (up to 21 mg iodine/mL solution) may be prepared and administered at a smaller volume. In conjunction with IV administration of iohexol: As 240 mg, 300 mg or 350 mg iodine/mL (diluted to 9-21 mg iodine/mL concentration): 180-750 mL. Use smaller volumes for higher concentrations. As 9 mg and 12 mg iodine/mL oral solution: 180-750 mL. Max total iodine dose: <3 years 5 g iodine; 3-18 years 10 g iodine. Doses may be given all at once or over 45 minutes if with difficulty in consumption.
Child: As 9 mg iodine/mL powder for oral solution (Oraltag®): <3 years 120-300 mL. Max total iodine dose: 4.5 g; 3-18 years 280-750 mL. Max total iodine dose: 9 g. Doses are given 20-60 minutes prior to image acquisition and will vary based on the size of the patient. If the patient has difficulty in consuming the required volume, a higher concentration of solution (up to 21 mg iodine/mL solution) may be prepared and administered at a smaller volume. In conjunction with IV administration of iohexol: As 240 mg, 300 mg or 350 mg iodine/mL (diluted to 9-21 mg iodine/mL concentration): 180-750 mL. Use smaller volumes for higher concentrations. As 9 mg and 12 mg iodine/mL oral solution: 180-750 mL. Max total iodine dose: <3 years 5 g iodine; 3-18 years 10 g iodine. Doses may be given all at once or over 45 minutes if with difficulty in consumption.
Oral
Gastrointestinal tract examination
Adult: As 350 mg iodine/mL solution (undiluted): 50-100 mL.
Child: <3 months As 180 mg iodine/mL solution (undiluted): 5-30 mL; 3 months to 3 years As 180 mg, 240 mg or 300 mg iodine/mL solution (undiluted): Up to 60 mL; 4-10 years As 180 mg, 240 mg or 300 mg iodine/mL solution (undiluted): Up to 80 ml; >10 years As 180 mg, 240 mg or 300 mg iodine/mL solution (undiluted): Up to 100 mL. Dosage recommendations and concentrations used may vary among countries or individual products. Refer to specific product guidelines.
Child: <3 months As 180 mg iodine/mL solution (undiluted): 5-30 mL; 3 months to 3 years As 180 mg, 240 mg or 300 mg iodine/mL solution (undiluted): Up to 60 mL; 4-10 years As 180 mg, 240 mg or 300 mg iodine/mL solution (undiluted): Up to 80 ml; >10 years As 180 mg, 240 mg or 300 mg iodine/mL solution (undiluted): Up to 100 mL. Dosage recommendations and concentrations used may vary among countries or individual products. Refer to specific product guidelines.
Oral
Contrast-enhanced computerised tomography of the pelvis
Child: As 9 mg iodine/mL powder for oral solution (Oraltag®): <3 years 120-300 mL. Max total iodine dose: 4.5 g; 3-18 years 280-750 mL. Max total iodine dose: 9 g. Doses are given 20-60 minutes prior to image acquisition and will vary based on the size of the patient. If the patient has difficulty in consuming the required volume, a higher concentration of solution (up to 21 mg iodine/mL solution) may be prepared and administered at a smaller volume.
Rectal
Gastrointestinal tract examination
Child: <3 months As 180 mg iodine/mL solution (undiluted): 5-30 mL; 3 months to 3 years As 180 mg, 240 mg or 300 mg iodine/mL solution (undiluted): Up to 60 mL; 4-10 years As 180 mg, 240 mg or 300 mg iodine/mL solution (undiluted): Up to 80 ml; >10 years As 180 mg, 240 mg or 300 mg iodine/mL solution (undiluted): Up to 100 mL. Larger volumes may be used. Dosage recommendations and concentrations used may vary among countries or individual products. Refer to specific product guidelines.




 Sign Out
Sign Out