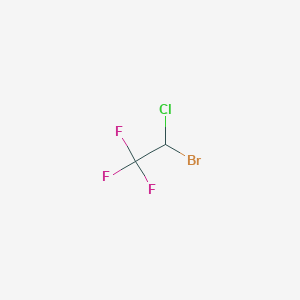
Induction and maintenance of general anaesthesia
Adult: Induction: 0.5% v/v of halothane in oxygen or mixture of nitrous oxide and oxygen, increase gradually according to response to a concentration of 2-4% v/v. Maintenance: 0.5-2% v/v depending on the flow rate used.
Child: Induction: 1.5-2% v/v. Maintenance: 0.5-1.5% v/v.
Child: Induction: 1.5-2% v/v. Maintenance: 0.5-1.5% v/v.




 Sign Out
Sign Out