Prophylaxis of Pneumocystis (carinii) jirovecii pneumonia
Adult: 1,500 mg once daily.
Oral
Mild to moderate Pneumocystis (carinii) jirovecii pneumonia
Adult: 750 mg bid for 21 days.
|
Indications and Dosage
Oral
Prophylaxis of Pneumocystis (carinii) jirovecii pneumonia Adult: 1,500 mg once daily. Oral Mild to moderate Pneumocystis (carinii) jirovecii pneumonia Adult: 750 mg bid for 21 days.
|
|
Administration
Should be taken with food.
|
|
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to atovaquone.
|
|
Special Precautions
Patient w/ GI disorders (e.g. diarrhoea, vomiting), pulmonary disease (due to causes other than pneumocystis pneumonia). Renal and hepatic impairment. Pregnancy and lactation.
|
|
Adverse Reactions
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, headache, cough; rash, pruritus, fever, anorexia, depression, dizziness, insomnia, hyponatraemia, elevated liver enzyme values, haematological disturbance (e.g. anaemia, neutropenia). Rarely, hypersensitivity reactions (e.g. angioedema, anaphylaxis, urticaria, vasculitis), cholestasis, hepatitis.
Potentially Fatal: Rarely, liver failure. |
|
Monitoring Parameters
Monitor hepatic function at baseline and during treatment. Assess patient’s food tolerance, post-dose vomiting and diarrhoea.
|
|
Drug Interactions
Decreased plasma concentration w/ metoclopramide, tetracycline, rifamycin derivatives (e.g. rifampicin, rifabutin), efavirenz or boosted protease-inhibitors (e.g. ritonavir). Slightly decreased plasma concentration w/ aciclovir, antidiarrhoeals, benzodiazepines, cephalosporins, laxatives, opioids, paracetamol. May decrease the rate of metabolism and increase the plasma concentration of zidovudine. May decrease the trough and area under the curve concentration of indinavir. May increase the plasma concentration of etoposide. May displace other highly protein-bound drugs from plasma-protein binding sites.
|
|
Food Interaction
Enhanced absorption w/ food.
|
|
Action
Description:
Mechanism of Action: Atovaquone, a hydroxynaphthoquinone, selectively inhibits the cytochrome bc1 complex (complex III) of the mitochondrial electron transport chain of a variety of protozoa and the parasitic fungus Pnuemocystitis jiroveci, resulting in the inhibition of nucleic acids and ATP synthesis. It is also used in combination w/ proguanil for the prevention and treatment of malaria caused by Plasmodium falciparum. Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Absorption is enhanced w/ food. Bioavailability: 23% (tab); 47% (susp). Time to peak plasma concentration: 1-8 hr and 24-96 hr. Distribution: Distributed into CSF (<1%). Plasma protein binding: >99%. Metabolism: Limited metabolism; undergoes enterohepatic recycling. Excretion: Via faeces (>94% as unchanged drug); urine (<1%). Plasma elimination half-life: 2-3 days. |
|
Chemical Structure
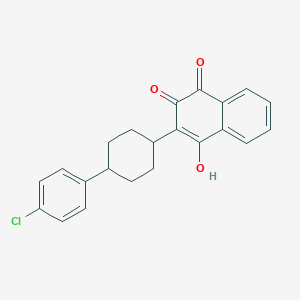 Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Database. Atovaquone, CID=74989, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Atovaquone (accessed on Jan. 21, 2020) |
|
Storage
Store between 15-25°C. Do not freeze.
|
|
MIMS Class
|
|
ATC Classification
P01AX06 - atovaquone ; Belongs to the class of other agents used in the treatment amoebiasis and other protozoal diseases.
|
|
References
Anon. Atovaquone. Lexicomp Online. Hudson, Ohio. Wolters Kluwer Clinical Drug Information, Inc. https://online.lexi.com. Accessed 14/10/2016. Atovaquone Suspension (Amneal Pharmaceuticals of New York, LLC). DailyMed. Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/. Accessed 14/10/2016. Buckingham R (ed). Atovaquone. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference [online]. London. Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 14/10/2016. Joint Formulary Committee. Atovaquone. British National Formulary [online]. London. BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press. https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 14/10/2016. McEvoy GK, Snow EK, Miller J et al (eds). Atovaquone. AHFS Drug Information (AHFS DI) [online]. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP). https://www.medicinescomplete.com. Accessed 14/10/2016.
|