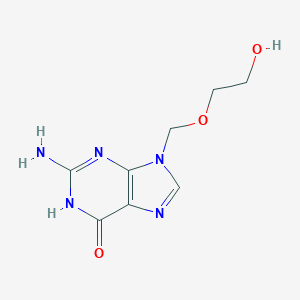
Recurrent herpes labialis
Adult: In immunocompetent patients: As delayed-release buccal tab: Apply 1 tab (50 mg) as a single dose to the upper gum region (canine fossa) within 1 hour following the onset of prodromal symptoms and before the appearance of any signs of herpes labialis lesions. Place the tab on the upper gum on the same side of the mouth as the herpes labialis symptoms. Do not apply the tab on the inside of the cheek or lip.
Intravenous
First episodes of genital herpes
Adult: For severe initial episodes in immunocompetent patients: 5 mg/kg 8 hourly via slow IV infusion over 1 hour for 5-7 days.
Child: ≥12 years Same as adult dose. Treatment recommendations may vary among countries and individual products (refer to specific local or product guidelines).
Child: ≥12 years Same as adult dose. Treatment recommendations may vary among countries and individual products (refer to specific local or product guidelines).
Intravenous
Varicella-zoster virus infection
Adult: Immunocompetent patients: 5 mg/kg 8 hourly via slow IV infusion over 1 hour for 5 days. Immunocompromised patients: 10 mg/kg 8 hourly via slow IV infusion over 1 hour for 5-7 days.
Child: 3 months to 12 years Immunocompetent patients: 250 mg/m2 8 hourly. Immunocompromised patients: 500 mg/m2 8 hourly. Treatment duration: 5 days. Alternative dosing for immunocompromised patients: <12 years 20 mg/kg 8 hourly; ≥12 years 10 mg/kg 8 hourly. Treatment duration: 7 days. All doses are given via slow IV infusion over 1 hour. Dosage recommendations may vary among countries and individual products (refer to specific local or product guidelines).
Child: 3 months to 12 years Immunocompetent patients: 250 mg/m2 8 hourly. Immunocompromised patients: 500 mg/m2 8 hourly. Treatment duration: 5 days. Alternative dosing for immunocompromised patients: <12 years 20 mg/kg 8 hourly; ≥12 years 10 mg/kg 8 hourly. Treatment duration: 7 days. All doses are given via slow IV infusion over 1 hour. Dosage recommendations may vary among countries and individual products (refer to specific local or product guidelines).
Intravenous
Mucocutaneous herpes simplex in immunocompromised patients
Adult: 5 mg/kg 8 hourly via slow IV infusion over 1 hour for 5-7 days.
Child: 3 months to 12 years 250 mg/m2 8 hourly for 5 days. Alternative dosing: <12 years 10 mg/kg 8 hourly for 7 days; ≥12 years Same as adult dose. All doses are given via slow IV infusion over 1 hour. Dosage recommendations may vary among countries and individual products (refer to specific local or product guidelines).
Child: 3 months to 12 years 250 mg/m2 8 hourly for 5 days. Alternative dosing: <12 years 10 mg/kg 8 hourly for 7 days; ≥12 years Same as adult dose. All doses are given via slow IV infusion over 1 hour. Dosage recommendations may vary among countries and individual products (refer to specific local or product guidelines).
Intravenous
Herpes simplex encephalitis
Adult: 10 mg/kg 8 hourly via slow IV infusion over 1 hour for 10 days.
Child: 3 months to 12 years 500 mg/m2 8 hourly, or 20 mg/kg 8 hourly; ≥12 years Same as adult dose. All doses are given via slow IV infusion over 1 hour. Treatment duration: 10 days. Dosage recommendations may vary among countries and individual products (refer to specific local or product guidelines).
Child: 3 months to 12 years 500 mg/m2 8 hourly, or 20 mg/kg 8 hourly; ≥12 years Same as adult dose. All doses are given via slow IV infusion over 1 hour. Treatment duration: 10 days. Dosage recommendations may vary among countries and individual products (refer to specific local or product guidelines).
Ophthalmic
Herpes simplex keratitis
Adult: As 3% eye ointment: Apply 1 cm ribbon of ointment inside the lower conjunctival sac 5 times daily at approx 4-hourly intervals. Continue treatment for at least 3 days after healing is complete.
Child: Same as adult dose.
Child: Same as adult dose.
Oral
Herpes zoster (shingles)
Adult: 800 mg 5 times daily at approx 4-hourly intervals (omit the night-time dose). Initiate therapy as early as possible following onset of rash. Treatment duration: 7-10 days. Consider IV dosing in severely immunocompromised patients or patients with impaired gut absorption.
Oral
Varicella
Adult: 800 mg 5 times daily at approx 4-hourly intervals (omit the night-time dose). Alternatively, 800 mg 4 times daily. Initiate therapy within 24 hours following onset of rash. Treatment duration: 5-7 days. Consider IV dosing in severely immunocompromised patients or patients with impaired gut absorption.
Child: ≥2 years weighing ≤40 kg: 20 mg/kg (Max: 800 mg) 4 times daily; >40 kg: Same as adult dose. Alternative dosing: <2 years 200 mg 4 times daily; 2-5 years 400 mg 4 times daily; ≥6 years 800 mg 4 times daily. Treatment duration: 5 days.
Child: ≥2 years weighing ≤40 kg: 20 mg/kg (Max: 800 mg) 4 times daily; >40 kg: Same as adult dose. Alternative dosing: <2 years 200 mg 4 times daily; 2-5 years 400 mg 4 times daily; ≥6 years 800 mg 4 times daily. Treatment duration: 5 days.
Oral
Herpes simplex infections of skin and mucous membranes
Adult: 200 mg 5 times daily at approx 4-hourly intervals (omit the night-time dose). Treatment duration: 5-10 days. Initiate therapy as early as possible after the start of infection. In severely immunocompromised patients or patients with impaired gut absorption: 400 mg 5 times daily for 5 days or consider IV dosing. Treatment or dosage recommendations may vary among countries and individual products (refer to specific local or product guidelines).
Child: <2 years Half the adult dose; ≥2 years Same as adult dose.
Child: <2 years Half the adult dose; ≥2 years Same as adult dose.
Oral
Suppression of recurrent herpes simplex
Adult: In immunocompetent patients: 400 mg bid at approx 12-hourly intervals, or 200 mg 4 times daily at approx 6-hourly intervals. Interrupt treatment every 6-12 months to reassess the condition. Episodic treatment of recurrent episodes: 200 mg 5 times daily at approx 4-hourly intervals for 5 days, preferably initiated during the prodromal period. Dosage recommendations may vary among countries and individual products (refer to specific local or product guidelines).
Oral
Prophylaxis of herpes simplex in immunocompromised patients
Adult: 200 mg 4 times daily at approx 6-hourly intervals. In severely immunocompromised patients or patients with impaired gut absorption: 400 mg 4 times daily or consider IV dosing.
Child: <2 years Half the adult dose; ≥2 years Same as adult dose.
Child: <2 years Half the adult dose; ≥2 years Same as adult dose.
Topical/Cutaneous
Herpes labialis
Adult: As 5% cream: Apply onto the affected area(s) 5 times daily at approx 4-hourly intervals for 4-10 days. Start treatment as soon as possible, preferably during the prodromal period.
Child: As 5% cream: Same as adult dose. Treatment recommendations may vary among countries and individual products (refer to specific local or product guidelines).
Child: As 5% cream: Same as adult dose. Treatment recommendations may vary among countries and individual products (refer to specific local or product guidelines).
Topical/Cutaneous
Mucocutaneous herpes simplex in immunocompromised patients
Adult: For limited non-life-threatening infections: As 5% ointment: Apply sufficient amount to cover all lesions 6 times daily at approx 3-hourly intervals for 7 days. Start treatment as early as possible after the onset of signs and symptoms.
Topical/Cutaneous
Genital herpes
Adult: As 5% cream: Apply onto the affected area(s) 5 times daily at approx 4-hourly intervals for 5-10 days. As 5% ointment: For management of initial episodes: Apply sufficient amount to cover all lesions 6 times daily at approx 3-hourly intervals for 7 days. Start treatment as soon as possible, preferably during the prodromal period. Treatment recommendations may vary among countries and individual products (refer to specific local or product guidelines).




 Sign Out
Sign Out